
by Luis Daniel Fernádez | Feb 28, 2025 | Equipment analysis
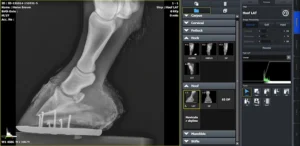
The model VIVIX-S 2530VW from the manufacturer Vieworks is a wireless flat panel detector for general radiography specifically designed for veterinary applications. It offers advanced technology with wireless connectivity and a lightweight, rugged and portable design with integrated handles, making it easy to carry and portable. Therefore, it stands out for being an indispensable tool in the area of diagnostic imaging to generate X-ray images with high precision and sharpness in small and large animals.
What are its main technical features, advantages and clinical applications? The following is an analysis of the equipment, detailing each of these aspects.
Technical characteristics of the VIVIX-S detector for veterinary use
This detector digital radiology The latest generation of combination of high-resolution technologya compact and portable design and a high resistance. At the same time, it is a multipurpose medical equipment that can be used in different environments, both in veterinary hospitals and in mobile clinics. Specifically, it has the following technical features:
Superior image quality
Thanks to its high Modulation Transfer Frequency Frequency (MTF) and Detection Quantum Efficiency (DQE), this detector provides accurate diagnostics and some images of X-rays with great clarity. With a pixel size of 124, the anatomical details of internal organs and tissues are visualized with a high definition. Therefore, it is a medical team that plays a key role in the evaluation of fractures, soft tissues and bone structures in animals.
Portable and lightweight design
The VIVIX-S 2530VW panel is easy to use and handleas it has a size 25.4 cm x 31.7 cm (11.5 in. x 11.5 in.) and a weight of 1.95 kg (including the battery). But, in addition to its ergonomic and lightweight design, it incorporates some handles for easy carryingadding convenience and comfort. This makes it a medical equipment ideal for all types of professionals, both those working in veterinary clinics and in field environments.

Strength and durability
It is designed to withstand harsh conditions and is equipped with the IP67 certificationwhich means that it is resistant to both dust and water. In addition, it offers a large temperature stabilityfrom 0 to 40 degrees Celsius.
To check your resistance and durabilityIt has been tested against drops of up to 1 meter and can withstand loads of up to 400 kg. Thus, it differentiates itself as a device that can be used in the veterinary diagnosis of large animals.
Long battery life and versatile charging
The 3400 mAh lithium-ion battery allows up to 1,250 exposures in a 15-second cycle and an autonomy of 8 hours in standby mode. In addition, it offers multiple loading optionsUSB-C connection, charging cradle and an innovative magnetic charging system, guaranteeing a continuous operation without interruption.
Advanced connectivity
It is equipped with Wi-Fi connectivity (802.11n/ac) and Gigabit Ethernet, so that the panel facilitates the fast image transmission without the need for cablesstreamlining the workflow in veterinary clinics. In addition, its integrated OLED display provides real-time information on battery and connection status.
Advantages of the VIVIX-S 2530VW panel
This flat panel offers multiple benefits for the veterinary medical team, optimizing the imaging process and improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Portability and ease of useThe lightweight design and the option of wireless connectivity allow it to be used in a variety of locations, from clinics to farms to animal rescue centers. For this reason, it is an equipment that can be used in veterinary examinations in different environments.
- High image qualityIts advanced image processing, using PureImpact™ technology, enhances image quality in contrast and sharpness. PureImpact™ is a post-processing algorithm that incorporates fine details without visual artifacts, such as soft tissue delineation, grid-free chest processing and clear, sharp resolution.
- Durability and resistanceRobust construction ensures reliable performance and increased durability, even under adverse conditions. For this reason, this device becomes a good long-term investment.
- Optimization of working timeRapid image capture and transmission reduces consultation waiting times, which translates into a better veterinary experience and care.
VIVIX-S integration with VXvue image acquisition software
On the other hand, it also includes integration with VXvuea digital radiographic image acquisition software specifically designed for the detectors of the Vieworks VIVIX-S series. This software offers a comprehensive solution for the acquisition and management of radiographic images, maximizing efficiency and accuracy in medical and veterinary environments. Its main functionalities are detailed below:
DICOM 3.0 compatibility
The DICOM medical image communication standard ensures efficient integration and communication with other medical imaging systems, facilitating data storage and transfer. It is responsible for the definition of the file format and structure and, at the same time, establishes a communications protocol to facilitate a proper connection between different medical equipment, devices and systems.
Integration with QXLink PACS system
At the same time, it can also be connected with the Vieworks QXLink PACS systemallowing for a centralized and secure management of medical imaging and patient data. Using a PACS systemdiagnostic images can be accessed anytime and anywhere via the Internet. It is therefore a key tool in medical diagnostics, as it offers great flexibility in the visualization of studies.
Advanced image processing with PureImpact™.
The PureImpact™ postprocessing algorithm provides a advanced image processing, increasing quality and resolution of radiographs. It excels in generating fine details without visual artifacts, accurate soft tissue delineation and elimination of grid lines, even in non-grid chest X-rays.
Automated functions
Includes tools such as image auto-assembly, automatic cropping, and automatic labelingThe new system is designed to streamline the image acquisition process and improve your operational efficiency.
Multi-task patient management
Allows you to manage multiple patients simultaneouslyThis facilitates the acquisition of images of different individuals in parallel.
Multilingual interface
The software is available in several languagesincluding English, Spanish, French, Italian, German, Russian, Chinese and Japanese, and offers the possibility of adding other languages according to the user's needs.
Optimized touch interface
This software is designed for your use on tablets and touchscreens. In addition, it features larger icons and fonts for intuitive operation, as well as specialized functions. These include gripper zoom and tactile scrolling.
Easy customization
Offers three types of image processing (soft, normal and hard) to suit the individual preferences of veterinary professionals. It also allows customization of themes and layouts, including automatic interface rotation for vertical monitors.
Optimization for various applications
The VXvue software is configured for its use in general human and veterinary radiography (with specific options for dogs, cats, exotic animals and equines) and mobile X-ray systems. Therefore, it is a software that adapts to the specific needs of each clinical environment.
Clinical uses and applications
The VIVIX-S 2530VW detector is a very versatile tool that adapts to various specialties within veterinary medicine. Some of its main applications include:
- Diagnostic imaging in small and large animalsHigh-resolution radiographs can be obtained to evaluate fractures, joint injuries, lung disease and internal organ abnormalities.
- Surgical proceduresIts ability to generate high-precision images in real time facilitates the work of veterinarians during orthopedic surgeries and invasive procedures.
- Dental examinationsThe detailed resolution of the panel is ideal for evaluating caries, infections and structural anomalies in the dentition of dogs, cats and horses.
- Orthopedic and neurological evaluationsIt is especially useful for detecting dysplasias, spinal conditions, joint problems and neurological lesions.
Conclusion
VIVIX-S 2530VW is a wireless detector for general radiography in veterinary medicine that has a high durability, portability and image quality. Its technology and innovation not only facilitates fast and accurate diagnosis, but also improves your efficiency in the clinical setting and veterinary practice.
At 4D Médica, we have this medical equipment specialized in the veterinary area.. If you are looking for a complete digital radiography solution that can be adapted to different uses, this flat panel is one of the best options on the market. Need more information? Contact with us and we will offer you personalized advice according to your needs.
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.

by Kiko Ramos | Feb 25, 2025 | News
The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) is an international organization that multidisciplinary professional organization which promotes research, education, and international collaboration in the cancer treatment in Europe and worldwide. Founded in 1975, it brings together physicians, researchers and health professionals who are responsible for implementing innovative strategies and developing medical advances in the area of oncology.
What are the latest advances that have been made in oncology in the last year? In the following article, we analyze the importance of ESMO in medicine and the most outstanding research in cancer treatment.
ESMO's role in medicine
ESMO plays a key role in cancer research worldwide. Among its main functions, it supports research into new therapies, the development of personalized medicine and the use of artificial intelligence in the detection of cancer and in the area of diagnostic imaging. It is responsible for the creation of various clinical guidelines to promote the medical education and research into innovative cancer treatments.
To this end, it organizes congresses, courses and scientific publications to update professionals and specialists on the latest trends in oncological treatments. At the same time, it also elaborates international guidelines and protocols for cancer diagnosis and treatmentThe company's work in this field has led to many advances: the following are some of the most important advances in the field In particular, its work in this field has led to many advances:
- Create and implement safer and more effective treatments.
- Promoting prevention by means of a early diagnosis of cancer.
- Promote a equitable access to cancer care.
- Improving quality of life of millions of patients.
4 new advances in oncology presented by ESMO
On an annual basis, ESMO organizes one of the most important oncology congresses in the world: the Congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology ESMO. It brings together researchers, professionals and world leaders in the field of oncology to present the latest discoveries in oncology therapies, prevention strategies and technological innovations in medicine.
The last event took place in Barcelona, Spain, from September 13 to 17, 2024, where it was possible to analyze the latest advances in cancer treatment. The following is a summary of what was new:
New studies in immunotherapy
As recently as 15 years ago, the prognosis for a patient with metastatic melanoma was very limited. There was no way to slow the progression of the skin cancer and their life expectancy was less than six months. However, at the beginning of the last decade, great advances were achieved with the development of immunotherapy.
What does immunotherapy consist of? It is a technique based on the stimulation of the body's own defenses to eliminate the malignant cells present in the body. Today, immunotherapy studies have achieved a survival rate of 10 years for a person with the same disease. Its favorable results have allowed it to be expanded to other tumors and, at present, it is also being used to treat other tumors. is used in some types of lung, bladder and breast cancer.
A decade later, it has become a fundamental therapeutic approach that is still under continuous development and research.. During the ESMO congress, a study was presented showing the long-term impact of immunotherapy. The publication showed that half of the patients with metastatic melanoma who had been treated with immunotherapy survived cancer-free for up to 10 years.
Another research presented at the congress was that this type of drugs raises the survival of the most aggressive breast cancer: triple negative.
2. Intelligent precision chemotherapy
One of the major innovations addressed at the ESMO 2024 congress is the ADC drug developmentwhich combine a monoclonal antibody with cytotoxic agents. These drugs allow targeting chemotherapy directly to tumor cellsThis increases efficacy and reduces side effects.
Currently, the intelligent chemotherapy, with greater precisionis one of the most outstanding advances in oncology treatment and cancer cure. The use of ADC drugs represents one of the most promising solutions for the treatment of cancer. to treat different types of tumors, applying lower doses of chemotherapy and with lower toxicity.
3. Artificial Intelligence applied to Oncology
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing oncologyThe results of this research range from predicting responses to treatments to detecting genetic alterations that are invisible to the human eye. The AI in medicine facilitates the realization of faster and more accurate medical testsThe company's products and services are designed to improve the personalization of therapies and optimize clinical results.
4. Shorter and more effective radiotherapy in breast cancer treatment.
According to a study presented at the ESMO annual congress, a shorter radiotherapy protocol proves effective for women with breast cancer. During the clinical investigation, 1,265 patients were evaluated and the effects of a standard five-week radiation therapy were compared with a new scheme, referred to as "hyperfractionated".. This protocol consisted of reducing the treatment to three weeks and increasing the irradiation dose progressively at each session.
Currently, it had been studied that the effectiveness of a shorter radiotherapy was the same in the case of a localized tumor, but it had not yet been analyzed in women with lymph node breast cancerwhich represents the 30% of breast cancers. As session doses increased, there were fears of increased side effects, but the results of the fractionated therapy study indicate increased overall survival rates without relapse and metastasis.
Thus, the future application of shorter radiotherapies in cases of nodal breast cancer will help to reduce the treatment load and increase its efficiency.
In conclusion
These advances and challenges presented at the ESMO 2024 congress reflect the dynamism and advances in the area of oncology and cancer treatment. To this end, they have a great importance of research and adaptation of clinical practices to improve patient outcomes and prognoses.
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.

by Kiko Ramos | Feb 19, 2025 | Curiosities
The discovery of X-rays was one of the most important scientific breakthroughs in history. The author of this discovery was the physicist Wilhem Conrad Röntgen, who accidentally discovered this technique in his laboratory in 1895. Over the years, it became a fundamental tool in the fields of medicine, industry and security. The old X-ray machines revolution in the health care sector, particularly in the area of diagnostic imaging. But what is the origin of this medical technique and how did the first X-ray machines come about?
Discovery of X-rays
X-rays were discovered the November 8, 1895 by physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgenin Hamburg, Germany. After his studies in medical engineering, he entered the world of physics and obtained his first findings while studying the penetrating power of cathode rays.
Throughout his research, he identified that a nearby fluorescent screen emitted a glow, even though there were solid objects between the radiation source and the screen. This phenomenon indicated that a new form of radiation, invisible to the human eyewas able to pass through opaque objects and project their image on a surface. Röntgen called it "X-rays", using the letter "X" to indicate that it was an unknown phenomenon.
How was the first X-ray created?
Röntgen, with the assistance of his wife, Anna Bertha Ludwigdiscovered that by holding a lead hoop he could see the bones of his wife's hand. along with her wedding ring. The physical decided to print the image and, to do so, he asked his wife to place her left hand on a metal plate so that he could photograph her, giving rise to the first X-ray.
Findings and initiation of radiological practice
At January 1896, Röntgen published his discovery in the article "On a new kind of rays". A few weeks later, the news spread rapidly around the world and, that same year, the first medical applications began to be developed.
This discovery revolutionized medicine and awarded Röntgen the first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.He was the first recipient in the history of these awards. Throughout history, several physicians applied X-ray radiation to treat dermatological conditions and some types of cancer, such as basal cell, uterine cancer and leukemia.
However, the first medical radiologist who did research on its application and the development of radiological practice was Albers-Schönberg. The author produced the first publication on radiology worldwide, entitled "Progress on X-ray areas". Subsequently, the first publications in the field of X-rays began to be developed. X-ray machines.
Antique X-ray machines: Origin, components and characteristics
Currently, X-rays represent one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging technologies. The electromagnetic radiations generated by X-rays have the ability to pass through organic matter and imprint it on a plate with photographic material. Subsequently, they generate medical images in shades of black, gray and white of the internal structures of the human body, giving rise to what is known as the radiography.
The use of this technology allows the diagnosis of multiple diseases and injuriesand, therefore is used in different medical techniques and equipmentBoth in its entirety and in combination with nuclear techniques. From conventional radiography, the computed tomography or CAT scanthe mammographyfluoroscopy and angiography to bone densimetry.
The first antique X-ray machines were based on the Crookes tube, a vacuum glass device that generated electrons from an electric current. These electrons struck a metallic material, producing X-rays, which could pass through soft tissues and project an image of bones onto a photographic plate.

Components of old X-ray machines
Early X-ray machines were made up of a series of essential components that allowed the generation and capture of images. Unlike modern equipment, the first devices were rudimentary and lacked safety measures, which implied certain risks for both operators and patients.
- Crookes tubeThey worked by means of a vacuum tube with electrodes that generated X-rays upon impact against a metallic material. To do this, they used electrical discharges in low pressure gases.
- High voltage sourceThis element was necessary to accelerate the electrons in the vacuum tube.
- Fluorescent screen or photographic plateIt was in charge of capturing the image projected by the X-rays.
- Manual exposure systemThere was no automatic control of exposure time, which generated a series of risks.
Characteristics of old X-ray machines
In addition to their components, early X-ray machines had several features that set them apart from today's equipment:
- Bulky and fragile structureThey were large and heavy equipment, with glass components that could break easily.
- Prolonged exposure to radiationTo obtain a clear image, patients had to remain still for up to 30 minutes, which increased their exposure to radiation.
- Absence of security measuresLead barriers and protection for operators or patients were not used, since the harmful effects of radiation were not known at that time.
- Low quality imagesThe first radiographs were blurred and with low contrast, which made medical interpretation difficult.
Evolution of X-ray machines
As the risks of radiation were understood, improvements in X-ray technology were introduced:
- 1913 - Coolidge TubeA new, safer and more efficient X-ray tube was developed, allowing better images with less exposure.
- 1920-1930 - Lead protectionLead aprons and protective barriers were implemented to reduce radiation exposure.
- 1970 - Digital radiographyIt allowed obtaining higher quality images with reduced exposure times.
- News - Advanced technologyToday, there are systems such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy and digital mammography, which offer high-precision images with minimal radiation doses.

Risks and limitations of early X-ray machines
Although X-ray machines represented a major breakthrough, they also brought together a set of limitations and dangers:
- High radiation levelsIn the absence of dose control, operators suffered burns and other harmful effects after repeated exposures.
- Burns and diseasesProlonged exposure could cause skin lesions, hair loss and even serious diseases.
- Lack of precisionThe images were of low resolution, which hindered accurate diagnoses.
- Unregulated useIn the early years, there were no regulations on the use of X-rays, which led to accidents and health problems.
Early X-ray machines were a milestone in medical historyHowever, their unregulated use and high level of radiation posed significant risks. Today, X-rays continue to be a major risk. essential tool for medical diagnosis. However, its multiple advances and the use of technology has made it possible to create modern, safe and much more efficient medical equipment for the detection of diseases and other conditions.
If you are interested in acquiring a X-ray equipment or any type of radiological equipment contact us and we will be happy to advise you and give you the best solution for your clinic or health center.
Contact 4D
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.

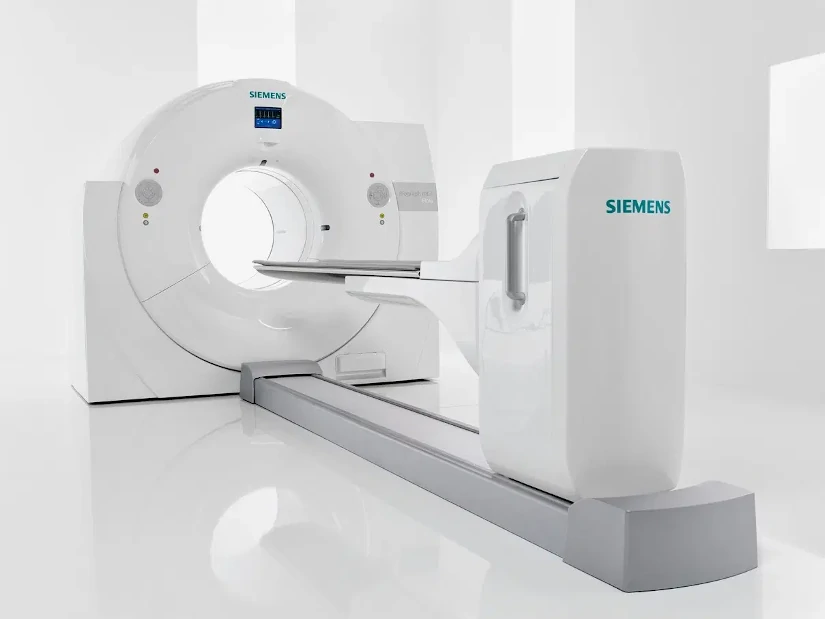
by Luis Daniel Fernádez | Feb 14, 2025 | Equipment analysis
The PET technique CT consists of the integration of two imaging technologies in the same medical equipment: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Axial Tomography (CT). The first PET-CT prototype was developed at the University of Pittsburgh in 1998 and its commercialization began in 2001, making it one of the first PET-CT scanners in the world. the most innovative and up-to-date equipment of the area of diagnostic imaging.
A PET CT system is a hybrid medical equipment with a stretcher and a shared medical image acquisition systemThe combination of both technologies provides a tomographic image that represents a cross-section of the organism, offering anatomical and functional information of the interior of the human body. The combination of both technologies provides a tomographic image that represents a cross section of the organism, offering anatomical and functional information of the interior of the human body.
On the one hand, the technology of Positron Emission Tomography or PET scanning provides functional and molecular information of the tissues through the use of a radiopharmaceutical. Therefore, it allows the quantification of various biochemical processes. From cellular metabolism, blood flow and protein synthesis to the analysis of different receptors. For its part, the Computed Axial Tomography or CT reports the different tissue densities generating a high-resolution anatomical image.
Thus, by combining the two techniques in a single integrated PET CT systemcan be generated anatomical and functional images simultaneously. As a result, more complete and efficient clinical diagnoses are offered, both in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Through its ability to detect functional alterations before they are visible in conventional studies, PET CT is fundamental in the early detection of diseases and in the evaluation of the effectiveness of treatments. Especially in enceological, neurological and cardiac diseases. In the following article, we analyze how it works and its main uses in clinical practice.
How does the hybrid PET CT equipment work?
The medical image acquisition protocol in a PET CT study is similar to the procedure for the standard PET technique. In a PET CT scanner, the acquisition of the study consists of three phases: the performance of a topogram, the performance of a CT study that will make it possible to determine the attenuation correction of the PET technique and, finally, the acquisition of the Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Each of these phases is discussed below:
Patient preparation
Before performing a PET CT study, the patient must be properly prepared so that the medical images obtained are of optimum quality. First of all, a radiopharmaceutical is administeredThe most widely used is Fluorine-18-labeled Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG). This compound makes it possible to detect areas of high metabolic activity that often arise in certain types of cancer, neurological and cardiac diseases. The radiopharmaceutical is administered intravenously and the patient must wait between 45 and 60 minutes for it to distribute correctly by the agency prior to the start of image acquisition.
For optimal uptake of the radiopharmaceutical, the patient must follow a series of medical recommendations:
- Fasting for at least 4-6 hours before the study.which avoids interference with glucose metabolism.
- Staying well hydrated before and after of the procedure.
- Control blood glucose levelsThe high levels may affect the uptake of the radiopharmaceutical.
- Follow instructions from physical rest before the study. Excessive movement prior to the study may generate unwanted FDG accumulation in the muscles.
- In some cases, a controlled breathing protocol to improve the quality of the CT image.
2. Positioning of the patient in the tomograph
Once the waiting period after injection of the radiopharmaceutical is over, the patient is placed on the bed of the PET CT scanner.. To obtain high quality images and reduce errors in PET and CT image superimposition, it is essential that the patient is well aligned and comfortable. In turn, The patient is asked to extend the arms over the head. if possible, to reduce interference in the images of the thorax and abdomen. On the other hand, metal objects are removed and elements that may affect image quality.
Subsequently, the position of the stretcher is adjusted according to the area to be examined, ensuring that the body is well aligned with the CT scanner detectors. In this process, patient immobility is crucial to avoid blurred images and improve diagnostic accuracy.
3. Making the topogram
The first step in the examination of the patient is to perform a topogram with the PET CT equipment. The images are obtained using the X-rays in a fixed position, which can be anterior, posterior, lateral or in an intermediate orientation. The acquisition is performed with a continuous movement of the stretcher in a predetermined range. In this way, a anatomical image similar to an X-ray projectionwhere the different internal structures and tissues can be analyzed.
It is important that during the procedure the equipment is adjusted and the limits of the PET CT study are defined. Depending on the model of the CT scanner, the fields of view and image formation may be different for different techniques. Therefore, it is necessary to verify that all body parts are within the image with the smallest field of viewwhich are normally those of the CT scan.
4. Elaboration of the TAC study
Once the field of view of the PET CT study has been defined, the patient's stretcher is automatically mobilized to start the CT diagnosis. In the test, a specific breathing protocol is introduced to match the CT and PET image, since the latter is acquired with normal breathing by the patient.
The duration of the CT study depends on various parameters: the extension of the area to be scanned, the rotation speed of the tube and the translation of the stretcher. CT allows detailed anatomical images to be obtained through the use of X-rays, which facilitates the precise localization of organs and structures. In some cases, a contrast medium may be administered to enhance the visualization of vascular structures or specific lesions.
Regarding its duration, a full body CT study using the hybrid equipment is less than one minute. This is because the images obtained are used for attenuation correction in the PET study, which significantly reduces the acquisition time. In PET equipment, when germanium (Ge) sources are used, the CT procedure time amounts to 20 to 30 minutes. With this, radiation exposure is reduced and the patient experience is improved.
5. Acquisition of the PET study
After the CT analysis, PET images are acquired, in which the metabolic data of the tissues are captured. For this purpose, the couch is moved to position the patient in the field of view of the PET scanner, encompassing different positions on the stretcher to cover the region of interest to be analyzed. All these areas are the ones that cover the range explored by CT.
The acquisition time of the PET study can range from between 10 and 30 minutes. This depends on the stretcher positions, the range scanned, as well as the equipment used. During this phase, the areas of the body with abnormal metabolic activity are highlighted on the PET imageThis makes it possible to detect tumors, infections or neurological problems with great precision.
6. PET CT image reconstruction
Reconstruction is performed in parallel to image acquisition.This allows results to be obtained in just a few minutes. This step is essential to generate highly accurate fused images, combining the metabolic information from PET with the detailed anatomical structure from CT.
In this process, the reconstruction time of each CT slice is less than one second.The PET images are reconstructed and available for analysis at the end of the acquisition of the last couch position. To achieve this, we use the reconstruction algorithms available in PET tomographs with the scatter and attenuation corrections determined from CT images.
7. Image analysis and interpretation
Once the images have been reconstructed, they are analyzed, where specialists can analyze different types of medical images:
- PET images without correctionThey show the uptake of the radiopharmaceutical in the body.
- Corrected PET imagesThey incorporate attenuation adjustments to improve accuracy.
- CT imagesThey offer anatomical details of the explored region.
The image fusion software allows the superimposition of PET and CT information, facilitating the exact localization of lesions and their subsequent analysis and interpretation.
What is PET CT used for?
It is a diagnostic technique that is essential in different medical specialties:
- OncologyEarly detection of tumors, evaluation of metastases and treatment follow-up.
- NeurologyIt is used for the diagnosis of diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and epilepsy.
- CardiologyThey play an essential role in the evaluation of blood flow and the detection of lesions and abnormalities in the heart.
- Immunology and infectionsHelps in the identification of inflammatory processes and infectious diseases.
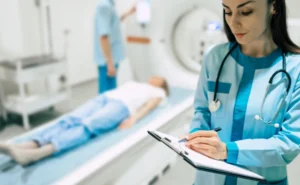
Source || Canva
Clinical applications of PET CT
PET CT technology combines the advantages of an anatomical and a functional imaging technique. In the current medical context, the use of this hybrid equipment is used in the following cases:
To confirm or rule out a malignant tumor pathology.
The PET technique can to analyze whether a lesion is benign or malignantThis can avoid the need for biopsies and other invasive diagnostic tests. In turn, it allows early detection of tumor processes, before anatomical changes occur that can be detected by morphological imaging techniques.
Determine tumor extent
It has the ability to perform whole body studieswhich makes it possible to rule out or confirm other malignant lesions concurrent with the primary tumor.
Detecting new tumor recurrences
Through this technique, it is possible to differentiate between malignant processes and new tumors that arise recurrently. This can be used to optimize patient treatment planning.
Assess response to treatment
The metabolic changes produced before an adequate response to chemotherapy are observed earlier in PET imaging than in other techniques. diagnostic imaging. Therefore, this type of medical imaging is an early indicator of tumor response. Their use helps to determine the continuation of certain treatments or, on the contrary, their interruption.
The use of hybrid PET-CT equipment is a crucial advance in medical diagnostics. It combines a functional and anatomical analysis of the inside of the human body in a single medical device, making it fundamental in the early diagnosis of cancer and other neurological and cardiological diseases. The combination of technology and medicine continues to save lives, and the PET CT technique is a clear example of this.
Bibliography
Instituto de Salud Carlos III (n.d.).
PET/CT Image Acquisition and Processing Handbook. REPISALUD. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from
https://repisalud.isciii.es/rest/api/core/bitstreams/5a1cd1bb-f736-4746-aa8c-0cc3a0a7a274/content
Medigraphic (2005). Acta Médica Article. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/actmed/am-2005/am053e.pdf
Electronic Journal of University Medical Science (n.d.). Article in RECIAMUC. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://www.reciamuc.com/index.php/RECIAMUC/article/view/1326/2074
Medigraphic (2014). Acta Médica Article. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/actamedica/acm-2014/acm141i.pdf
Martínez del Valle, M. (2016). PET-CT: Physical basis, instrumentation and technological advances. Radiology, 58(5), 377-389. Elsevier. Retrieved from https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-radiologia-119-articulo-pet-tac-bases-fisicas-instrumentacion-avances-S0033833816301801?newsletter=true
Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SEMNIM). (2019). PET-CT protocol. SEMNIM. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://www.semnim.es/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/79.pdf
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.


by Kiko Ramos | Feb 10, 2025 | News
Millions of cases of cancer are diagnosed every yearbeing the second leading cause of death in the world. The term cancer encompasses numerous diseases characterized by the development of abnormal cells in the body that divide, grow and spread uncontrollably throughout the body. It encompasses more than 200 types of cancerThe main ones are breast, lung, colon and rectal (colorectal), prostate, skin, liver, pancreatic, cervical, stomach and blood (leukemia) cancers.
The World Cancer Day is celebrated on February 4.where prevention and early detection is a key aspect in the fight against the disease. Early diagnosis can save many lives and, in this area, the area of diagnostic imaging plays an essential role.
Through the use of advanced technologiesIn addition, it is possible to identify abnormalities before symptoms or signs appear by means of computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), mammography and other support techniques. In addition to this, it is possible to medical innovation and use of artificial intelligencewhich allows for a much more accurate, personalized and efficient diagnosis. This not only improves success and survival rates, but also facilitates less aggressive and more effective treatments.
Importance of early cancer diagnosis
The early diagnosis of cancer is an essential tool for detecting the disease in its early stages. Many cancers are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms that may go unnoticed. However, when detected early, cancer treatments tend to be more effective and less aggressive, so that survival rates increase significantly.
For example, in the case of breast cancer, the five-year survival rate is higher than 90% when detected at an early stage, while in advanced stages the chances of success are drastically reduced. The same is true for colon, prostate, lung and cervical cancer, among others.
What are the main advantages of early diagnosis?
- Increased treatment effectivenessTreatments are more effective at earlier stages, reducing the need for invasive procedures such as aggressive surgery or intensive chemotherapy.
- Reduced impact on quality of lifeDetecting cancer early may allow for less aggressive treatments with fewer side effects.
- Increased survival rateIn many cases, patients who receive an early diagnosis have a much longer life expectancy.
- Reduction of healthcare costsCancer treatment in advanced stages is more costly and complex. In contrast, early detection allows for simpler and more economical interventions.
Diagnostic Imaging: Benefits in Cancer Screening
The diagnostic imaging area allows non-invasive observation of the inside of the body through the use of different technologies, tools and specialized medical equipment. This is crucial in the detection of cancer, since facilitates the identification of organ and tissue abnormalities. The main benefits of diagnostic imaging in the early detection of cancer include:
Early detection of tumors before they become clinically apparent
One of the greatest benefits of diagnostic imaging is its ability to detect tumors in early stages, when there are no symptoms or signs yet. that evidence the presence of tumors or irregularities. Thus, by starting treatment early, your success rates are increased.
Accurate assessment and reduction of invasive procedures
Medical imaging provides a more accurate detailed visualization of body organs and tissuesThis helps specialists to differentiate between benign and malignant masses. With this, it is possible to to accurately assess the size, location and characteristics of the tumor. In turn, the need for invasive procedures is reducedas in the case of biopsies.
Monitoring of disease progression and response to treatment.
Diagnostic imaging is not only used to detect cancer, but also to make a monitoring of patients' response to treatment. For this purpose, magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography (PET) tests make it possible to assess whether a tumor is responding correctly to chemotherapy, radiotherapy or immunotherapy treatments. In this way, it is possible to adjust the treatment according to the patient's needs.
Improvement of the patient's quality of life
Imaging studies, being non-invasive techniques, allow for the following detecting cancer without painful procedures or long recovery periods. This improves the patient experience and avoids unnecessary interventions in many cases, improving their quality of life.
Main imaging techniques for cancer detection
There are different medical techniques in the area of diagnostic imaging that play a key role in the detection of different types of cancer:
Mammography
Mammography is the main technique used in the diagnosis and treatment of early detection of breast cancer. By means of a mammography equipment or mammographer, tumors, microcalcifications and suspicious nodules can be identified before they are palpable. We can differentiate two types of tests:
- Screening mammogramsMammography: This is a screening used in women who have no signs or symptoms of breast cancer. Therefore, it is recommended that women over the age of 40 have this type of mammogram as a form of prevention.
- Diagnostic mammogramsBreast cancer screening: It is used when a woman has symptoms such as lumps, pain, discharge or changes in the skin of the breast, or when an abnormality is detected on a screening mammogram or screening mammogram.
Computed Tomography (CT)
Computed tomography, also known as computed tomography, also known as TACis a medical procedure that uses x-rays and digital processing to obtain detailed images of internal organs. It is essential in the screening for lung, liver, pancreatic and colon cancer.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
In this technique, a magnetic field is used to generate radio waves that allow to create detailed medical imaging of soft tissues. The magnetic resonance imaging is especially useful in the brain, prostate and breast cancer screeningThe results of the tumor assessment are more accurate.
Ultrasound
The ultrasound is a medical procedure that uses ultrasound waves to examine internal organs and structures. This is a key tool in the thyroid, ovarian and prostate cancer screeningIt allows the visualization of abnormal masses without radiation.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
The Positron Emission Tomography or PET scanning is a technique that uses a radioactive tracer to identify active cancer cells. It is used in the detection of metastases and in the evaluation of the response to treatment of oncology patients.
Colonoscopy with digital imaging
Allows you to detecting polyps in the colon and rectum that may progress to cancer. The use of colonoscopy in screening programs has significantly reduced colorectal cancer mortality.
The role of technology and Artificial Intelligence in early diagnosis
The advances in technology and the use of the artificial intelligence in medical image analysis are revolutionizing cancer detection. AI-based technologies can analyze mammograms, MRIs and CT scans with high accuracy, making it possible to identify patterns and abnormalities before symptoms become apparent.
The artificial intelligence systems in medicine use advanced algorithms and machine-learning models to analyzing medical images, medical records, genetic data and other sources of information of patients. The use of the AI in medicine improves diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in medical and health care, as large volumes of data can be analyzed quickly and accurately. As a result, it has become a key tool for early disease detection.
Main advantages of AI in cancer diagnosis
- Streamlines the performance of diagnostic imaging studies and interpretation of medical images.
- Offers more detailed and customized analysis for each patient.
- Helps reduce errors.
- Optimizes treatments to suit the needs of each patient.
- Improved health and hospital care.
In the fight against cancer, every small step counts. Prevention, early detection and the use of technology and medical innovation are the most important elements in advancing research into the disease and improving patients' quality of life.
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.












