por Luis Daniel Fernádez | Jan 31, 2025 | Equipment analysis
The positron emission tomography (PET) scanning is the technique of diagnostic imaging more recent and modern. It is a nuclear medicine procedure that emerged in the 1970s in the United States and was introduced in Spain in 1995. To perform a positron emission tomography scan, a radioactive material, called a radiopharmaceutical, is administered intravenously and the diagnosis is then made using specific equipment: the PET scanner.
This medical device is equipped with a special camera that allows visualization of internal organs at the molecular and cellular leveloffering information on metabolic activity of the body's tissues. From the analysis of blood flow, oxygen consumption, glucose and protein metabolism, amino acid transport and cell division to the detection of biochemical changes.
In the PET technique, radioation is detected after administration of the radiopharmaceutical. To do this, you need a waiting time between 30 and 60 minutes for the substance to take effect and be distributed correctly throughout the patient's body. This diagnostic imaging test is used for to develop a metabolic study of the interior of the organismIt therefore provides a complement to the anatomical information offered by procedures such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
One of the most recent advances in this area has been the development of hybrid equipment that combines two technologies in the same medical equipment. In 1998, the CT scanner began to be used in clinical practice. PET CTa device that incorporates the PET technique together with CT. A year earlier, in 1997, the hybrid PET MRI device was created by Mardsen and Cherry, which combines the anatomical images provided by MRI with the biochemical data from PET. However, it was not until 2009 that Phillips developed the first integrated system.
Currently, the use of positron emission tomography (PET) has made it possible to diagnose diseases in their earliest stages and, in turn, analyze the patient's response to specific treatments. Its ability to analyze functional changes before structural damage occurs in the body makes it key in the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple pathologies, especially in oncology, neurology and cardiology.
In the following article, we will analyze what this diagnostic technique consists of and the medical equipmentThe advantages and disadvantages, as well as their applications in clinical practice.
How does PET positron emission tomography work?
The positron emission tomography diagnosis consists of a process made up of different stages, which we analyze below:
Administration of the radiopharmaceutical
The first step in a PET study is the administration of a radioactive substancecalled radiopharmaceutical or radiotracer. This compound is generally introduced into the body intravenously, although in some cases it can be administered by inhalation or orally.
The most commonly used PET radiopharmaceutical is fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). It consists of a glucose-like molecule that is labeled with fluorine-18, a radioactive isotope. The main reason for using FDG is that cells with high metabolic activity, such as cancer cells, consume more glucose than normal tissues. This allows the radiopharmaceutical to accumulate in areas of higher cellular metabolism, facilitating its detection.
2. Distribution and waiting
After administration of the radiopharmaceutical, the patient must remain at rest for 30 to 60 minutes for the substance to be adequately distributed throughout the body. During this time, it is recommended that the patient remain calm and avoid talking or moving excessively, since muscular activity could alter the uptake of the radiotracer and affect the quality of the images.
3. Patient positioning
Once the radiopharmaceutical has been absorbed by the tissues, the patient is placed on a sliding stretcher which introduces it into the PET scanner.. This equipment consists of a ring of detectors that surrounds the patient and is capable of recording the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceutical. The procedure has a duration between 15 and 45 minutesdepending on the type of study to be performed.
4. Diagnosis by PET scanner
The radiopharmaceutical injected into the patient emits positrons.which collide with the body's electrons, generating two gamma photons in opposite directions. The PET scanner detectors capture these gamma photons and record the exact location of each emission. Subsequently, the medical team is responsible for the reconstruction of a tomographic image detailed with the areas where the radiopharmaceutical has accumulated, reflecting the metabolic activity of tissues and organs.
5. Image processing and reconstruction
Once the data has been collected, specialized software processes the information and generates three-dimensional images of the distribution of the radiopharmaceutical in the patient's body. These images show the areas of increased metabolic activity (hyper uptake) in brighter colorswhile areas with lower metabolism appear in darker shades. This activity map allows physicians to accurately identify anomalies such as malignant tumors, neurodegenerative diseases or cardiac conditions.
6. Analysis and interpretation of results
Finally, specialists in radiology or nuclear medicine analyze the images. obtained to make a diagnosis. Depending on the case, the PET scan can be combined with other imaging techniquesas the computed tomography (CT) or the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)as well as the use of hybrid equipment. This will provide a more complete view of the anatomy and function of the organs.
Source || Canva
Positron emission tomography advantages
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a highly advanced imaging technique with the following benefits:
Early detection of diseases
Allows you to identify metabolic abnormalities before visible structural changes occur in other imaging tests, which facilitates the early diagnosis of diseases. These include cancer, Alzheimer's disease and heart disease.
Real-time functional evaluation
In contrast to computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which only analyze anatomy, PET provides information on how tissues and organs function at the cellular and molecular level.
Effective technique to detect cancer and metastases
PET is one of the most effective tools for the detection and localization of cancer and its metastasesThis allows us to know the extent of the disease and to plan the appropriate treatment.
Monitoring treatment response
This is a diagnostic technique used for evaluate how a patient is responding to chemotherapy, radiotherapy or immunotherapy treatments. In this way, it makes it possible to make adjustments to the therapeutic strategy in real time.
Combined technology for greater precision
The use of hybrid equipment allow both anatomical and functional information to be obtained at the same time. At present, PET-CT and PET-MRI equipment offer the most advanced benefits of using two techniques in a single study. Its use helps to improve diagnostic accuracy and radiation dose reduction received by the patient by up to 50 %.
Disadvantages of positron emission tomography
However, it also has a number of limitations that are important to analyze:
Exposure to ionizing radiation
The PET technique uses radioactive radiopharmaceuticals that expose the patient to ionizing radiation. Although its doses are low and safe, the amount of radiation increases significantly when using various diagnostic techniques.
High cost and limited availability
It is a expensive technique because of the need for specialized equipment and the use of radiopharmaceuticals. These substances require rapid distribution in order not to lose effectiveness. Therefore, one of their disadvantages is that they limit availability in certain hospitals and regions.
Waiting time and duration of the study
Before performing the PET scan, patient must wait 30 to 60 minutes after injection of the radiopharmaceutical. Thus, in comparison with other diagnostic techniques, waiting time increases the duration of the test.
Complex interpretation of images
Medical images obtained can be difficult to interpret.not all elevated glucose uptake indicates abnormalities. Therefore, alternative tests are required for a more accurate diagnosis.
Clinical uses and applications
Positron emission tomography is used in different medical specialties, specifically in oncology, neurology and cardiology. What are its main uses in clinical practice?
Oncology
- Early detection of malignant tumors.
- Identification of metastases and evaluation of cancer spread.
- Assessment of the response to treatment with chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- Differentiation between benign and malignant tumors.
Neurology
- Early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer and Parkinson.
- Localization of epileptic foci in patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy.
- Evaluation of psychiatric illnesses and neurocognitive disorders.
Cardiology
- Determination of cardiac muscle viability in patients with myocardial infarction.
- Evaluation of blood flow and cardiac function in ischemic diseases.
Other medical applications
- Diagnosis of endocrine diseases, such as adrenal gland disorders.
- Detection of infections and chronic inflammatory diseases.
- Evaluation of gastrointestinal pathologies with metabolic involvement.
Conclusion
After analyzing the operation of positron emission tomography (PET), we can highlight that it is a fundamental tool in nuclear medicine to detect diseases in their early stages and evaluate the metabolic function of different organs and tissues.
Do you want more information about PET equipment? Contact us and we will offer you personalized advice to analyze the medical equipment you need in your clinic or hospital.
Contact 4D
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.


por Kiko Ramos | Jan 24, 2025 | AI in medicine
The use of Artificial Intelligence (IA) is transforming medical care in laboratories, clinics and hospitals. Through the use of technology, patient care can be improved, laboratory analysis processes can be optimized and diagnostic imagingas well as offering more efficient hospital management.
Artificial intelligence uses various algorithms that enable highly complex reasoning processes to be carried out, automating many tasks and functions. The use of AI in medicine provides multiple benefits and has a key role to play in the implementation of disease prevention and diagnosis, search for novel treatments and improvements in patient prognosis.
In the following article, we explain the process for implementing Artificial Intelligence solutions in laboratories, clinics and hospitals and the different applications that currently exist.
How to implement AI in laboratory and hospital analysis
Before starting to use artificial intelligence in the clinical setting, it is important to have an well-defined and structured strategy that integrates the technology along with the correct development of the process. These are the main steps to implement AI effectively:
1. Define the main objectives
The first step is to establish the objectives to be achieved with the integration of AI in the healthcare center. Among them, we can highlight:
- Reduction of diagnostic times.
- Customize treatments.
- Optimize resource management.
- Improve patient experience and care.
By setting clear goals, specific solutions can be provided using artificial intelligence, which will enable optimize healthcare management and save time and resources.
2. Analyze weaknesses and needs
Once the main objectives have been set, it is essential to carry out a complete diagnosis of the laboratory, clinic or hospital to analyze its weaknesses. This analysis should include the review of workflows the identification of the most important main problems and the areas that have a greater administrative or technical burden.
On the other hand, it is also important to involve medical, administrative and technical personnel in this process, as their day-to-day experiences provide a more accurate picture of real needs. Through a collaborative approach, AI solutions will be aligned with the specific challenges faced by the organization.
Select the right AI tools and solutions.
Subsequently, you must selecting the artificial intelligence technologies best suited to the hospital area. AI tools are revolutionizing the healthcare sector, especially in hospitals and laboratories, by improving diagnostic accuracy, increasing operational efficiency and delivering better healthcare. In this process, it is important to research the options available in the market and work with specialized healthcare technology providers.
Ensure proper integration into the healthcare ecosystem.
For the successful implementation of AI, it is crucial that new technologies are integrated with the systems that were already in use previously. Some of the tools we can highlight are hospital management software and its linkage with medical equipment, as well as the RIS system and the PACS system.
One of the essential aspects to achieve a correct integration is the interoperability concept. It refers to the importance of systems being compatible and capable of sharing information so that they can work in a coordinated and joint way in the different processes. For this reason, before applying the use of artificial intelligence, it is necessary to check that the systems to be used are compatible with each other.
5. Staff training
Another element to be taken into account is to provide a adequate staff training who will work with these technologies. This includes both medical and administrative staff, as they will be in charge of managing the tools, interpreting the data provided by AI and making the most of them in their day-to-day work.
In addition, it should fostering a culture of trust in technologyHe stressed that AI will not replace professionals, but is a tool that complements and improves their work. With this, it will be possible to ensure a correct transition to the application of new processes and innovations.
6. Ensuring data security and privacy
The management of medical data involves a great responsibility in terms of security and privacy. The implementation of AI must comply with local and international regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. In this way, it will be possible to ensure that patient information is protected at all times.
The main measures include the correct data encryption, a user authentication and the anonymization of information whenever possible. In addition, it is crucial to conduct regular audits to identify and correct possible vulnerabilities in the systems.
7. Implement in a staggered manner
Introducing AI gradually is a fundamental strategy for minimize disruptions to day-to-day operations and facilitate staff adaptation. You can start with a pilot project in a specific unit, such as radiology, and evaluate its impact before extending the implementation to other areas.
During this phase, it is important to collect feedback from staff and adjust the tools according to their needs and suggestions. Through this step-by-step approach, improvements can be made progressively and achieve a adequate adoption of new artificial intelligence tools.
8. Monitor and measure results
The implementation of AI must be accompanied by an continuous monitoring to ensure that the solutions are meeting the established objectives. This involves define key performance indicators (KPIs)The results of this study have been significant, such as a reduction in diagnostic time, an increase in operational efficiency and an improvement in patient satisfaction. Regularly evaluate these results will identify areas for improvement and adjust strategies as needed, taking full advantage of the benefits of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
9. Promote continuous innovation
The implementation of AI is not an isolated action, but rather a continuous process. Technology is a sector that is constantly evolving. Therefore, it is important to be aware of new tools and methods in the healthcare area in order to be able to implement future improvements. To ensure that a medical institution is committed to innovation and is competitive in its sector, the following can be done to promote various actions. Among them, we can highlight:
- Foster a culture of innovation among the personnel.
- Participate in research programs.
- Collaborate with universities or technology companies.
- Implement new tools and methods.
Artificial intelligence solutions for laboratory analysis, clinics and hospitals

Source || Freepik
What kind of solutions can be implemented to optimize clinical and hospital management?
Software with artificial intelligence
Through the use of a AI softwareon the same platform, you can storing medical images generated in diagnostic imaging studies, manage patient data in real time, generate automated reports and make comparisons of current studies with previous medical imaging.
AI-assisted diagnostic imaging
The current medical equipment can integrate diagnostic imaging software with AI. These systems employ advanced algorithms to identify anomalies and diseases early, improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce analysis time. They can be used for different types of equipment, ranging from X-raysCT scans, CT scans or TAC, ultrasounds y mammograms to magnetic resonances.
Virtual agents for laboratory analysis and hospital centers
A virtual agent provides automation of different tasksIt can therefore be implemented in the healthcare sector to optimize the management of medical centers, clinics and laboratories. Through an artificial intelligence platform such as Serenity Star AIcan be implemented chatbots and virtual assistants that offer 24-hour patient support, improving customer service. Among its advantages, it stands out for providing instant information on hospital services, resolving patient queries, guiding patients in their search for specialists, and managing appointments and other administrative procedures.
The use of virtual agents also offers other functions very useful in research and hospital management. They allow the analysis of complex medical data with high accuracywhich allows accelerate the performance of medical studies and develop improvements and innovations in areas such as research and laboratory analysis.
Laboratory process automation
There are AI systems that allow automate many functions in laboratory analysis processes. From the performance and analysis of clinical tests to inventory management and the implementation of quality control improvements. Its use helps reduce human error, increase operational efficiency and reduce study processing time.
AI-assisted surgical robots
In the field of surgery and interventional radiologyAI and robotic systems are marking a before and after. The use of AI-assisted surgical robotsas Da Vinci, help to realize more precise and less invasive procedures, decrease surgical risk and reduce recovery times of patients.
Another of the most noteworthy advances in this area is the creation of surgical simulation models to plan, practice and refine procedures before performing them in clinical practice.
Advances in telemedicine: Use of portable and AI-integrated medical equipment
Among the latest innovations, we can highlight the development of portable and AI-integrated medical devices. Its use offers continuous monitoring of patients outside the hospital environment, achieving great advances in telemedicine.
The telemedicine is one of the most outstanding areas of medical innovation, as it allows for assisting people with chronic diseases remotely and reach regions where medical services are not fully available. In this way, regardless of the specialist's location, fast and accurate diagnoses can be made.
Conclusion
Implementing artificial intelligence in laboratories, clinics and hospitals is a process that requires planning, collaboration and a strategic vision. From identifying needs to monitoring results, each step is crucial for ensure that AI is integrated effectively and generates tangible benefits. With proper execution, AI can transform healthcare, improving service quality, optimizing resources and ushering in a new era in healthcare management.
Do you need more information about software solutions for diagnostic radiology? Contact us to implement AI in the hospital environment.
Contact 4D
Bibliography
Castro Beltrán, J., Vivas Gamboa, R. C., & Caicedo, J. (2023). Artificial intelligence in medicine: A narrative review on advances, applications and limitations.
Risaralda Medical Journal, 29(2), 101-110. Retrieved from
https://ojs2.utp.edu.co/index.php/revistamedica/article/view/25606
Díez-Peña, E. (2023). Artificial intelligence in medicine: present and future. Andalusian Journal of Medical Electronics and Robotics, 8(4), 30-37. Retrieved from https://www.rade.es/imageslib/PUBLICACIONES/ARTICULOS/V8N4%20-%2012%20-%20CON%20-%20DIEZ_IA%20medicina.pdf
Martínez-González, L. (2023). Applications and challenges of artificial intelligence in the medical sector. Journal of Medicine and Health, 15(3), 45-55. Retrieved from https://remus.unison.mx/index.php/remus_unison/article/view/178
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.

por Kiko Ramos | Jan 17, 2025 | Equipment analysis
The radioprotection is the set of measures, standards and practices aimed at protecting people, the environment and the surroundings from the harmful effects of ionizing radiation. In the clinical setting, the aim of radiation protection is to ensuring the safe use of radiation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures for patients and healthcare personnel, minimizing the associated risks.
What is radioprotection?
The ionizing radiation is a fundamental tool in modern medicine. It is used in procedures of diagnostic imaging that use X-rays, such as conventional radiography, digital radiology, fluoroscopy, computed tomography (CT) and interventional radiologyRadiology, a branch of radiology that diagnoses and treats various pathologies by means of minimally invasive procedures. In turn, it is also used in radiotherapy treatmentsThe aim of this program is the destruction of tumor cells and tissues by means of radiation, and in the nuclear medicine.
However, its improper or excessive use can have harmful consequences for people's health.. These include tissue damage or increased risk of cancer in the long term. For this reason, it is of great importance in the clinical environment and requires a sound management. In this sense, the discipline of Radiation ProtectionThe company, which employs professionals such as physicists, physicians, biologists and engineers, is working to ensure that the development and application of technologies that use ionizing radiation are safe.
Basic principles of radiation protection
The Radiation Protection System is based on three fundamental principles that have been established by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP):
1. Justification
Any procedure involving the use of ionizing radiation must be medically indicated. This means that the benefits of the procedure must clearly outweigh the risks associated with radiological exposure.
2. Optimization (ALARA Principle)
Exposure should be kept "as low as reasonably achievable". This principle is referred to as ALARA and ensures that the lowest dose necessary to obtain clinical results is used.
3. Dose limitation
Strict dose limits must be established to protect both healthcare personnel and patients, preventing exposure from exceeding levels considered safe. This principle is oriented to the protection of persons exposed to radiation sources.
Application of the Radiological Protection System in the clinical environment.
In the clinical environment, the Radiation Protection System is implemented through a structured approach that includes the following aspects:
Design and maintenance of installations
The rooms of X-raysCT scans, CT scans or TAC and radiotherapy must be equipped with adequate shielding that minimizes radiation scattering. In turn, it is essential to carry out periodic inspections to guarantee the correct functioning of medical equipment and that they do not emit an unnecessary dose of radiation.
Equipment quality control
The following must be implemented preventive maintenance and calibration programs to ensure that the equipment operates efficiently within the established limits. Another key aspect is incorporate advanced technologies that allow automatic adjustment of radiation doses according to the patient's characteristics. To this end, digital radiology medical equipment will make it possible to optimize the amount of radiation, increasing safety in the healthcare environment for both medical staff and patients.
Staff training
One of the strategies to promote radioprotection in the clinical setting is to to train health professionals on the safe use of medical equipment that emit ionizing waves and which, in turn, have knowledge of the three principles of radioprotection. In this way, through appropriate training, it will be possible to promote the development of a safety culture to ensure the application of good practices in daily work in the health sector.
Radiation protection measures
Radiation protection in the clinical environment is essential to ensure the safety of patients and healthcare personnel from the risks associated with ionizing radiation. To this end, various strategies and tools designed to minimize unnecessary exposure are implemented, respecting the principles of justification, optimization and dose limitation.
Protection of healthcare personnel
Personnel working in areas where ionizing radiation is used must be adequately protected to avoid cumulative exposure that may pose a long-term risk. Key measures include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)Professionals should wear leaded aprons, thyroid protectors, leaded goggles and gloves that are specifically designed to reduce direct exposure to radiation.
- Dose monitoringIt is mandatory for health personnel to record the amount of radiation accumulated. This monitoring ensures that the dose does not exceed the limits established by the regulations in force.
- Staff turnoverTo minimize exposure time, personnel rotation is organized in tasks involving the handling of radiation-emitting equipment. In this way, the exposure load is evenly distributed.
Get to know our 4D Médica protection equipment
Patient protection
Patients should also be protected from unnecessary radiation exposure, especially considering that they are often exposed in a timely manner but with high doses in some diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. The most relevant measures are:
- CollimationIt is essential to limit the area of the body that is exposed to radiation by using collimation systems that focus the radiation beam only on the area of interest. This reduces the amount of tissue irradiated and thus the associated risks.
- Optimized protocolsModern equipment makes it possible to adjust the exposure parameters (such as energy and radiation time) according to the specific characteristics of each patient. This makes it possible to deliver a minimum dose without compromising the quality of the radiation dose. medical images or treatment.
- Repetition controlTo avoid unnecessary repetitions of radiological studies, it is essential that the staff is well trained and that the equipment is functioning optimally. This ensures that the images obtained are of diagnostic quality on the first attempt.
Signaling and delimitation of areas
Facilities using ionizing radiation must have proper signage and access control to protect those not involved in the procedures. These measures include:
- SignageVisible signs should be posted indicating radiological risk areas and exposure levels, warning people of the need to wear appropriate protection or to avoid entry.
- Delimitation of areasIonizing radiation: Access to areas where ionizing radiation is used should be restricted. Its use should be limited to authorized personnel, thus avoiding accidental exposure of third parties or the general public.
Conclusion
The radioprotection in the clinical environment is a shared responsibility that requires the collaboration of professionals, patients and regulatory bodies. Applying protection principles and measures not only ensures safety, but also improves the quality of medical care.
If you want to get more information about protective equipment or medical diagnostic equipment, you can contact us. Our 4D team will advise you to find the best solution for your clinic or hospital.
Contact 4D
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.

por Luis Daniel Fernádez | Jan 16, 2025 | Equipment analysis
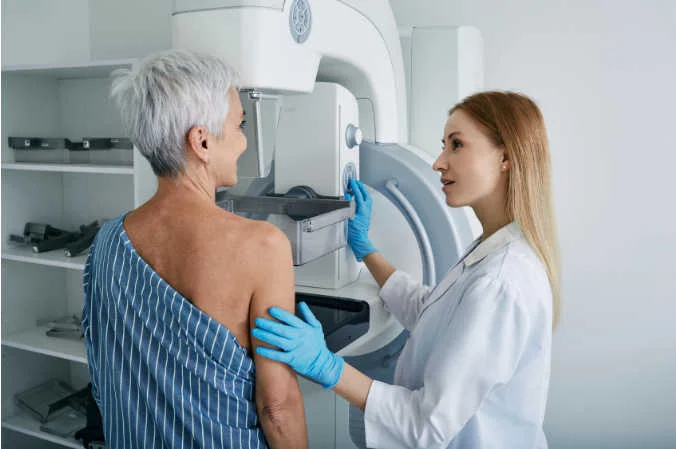
The mammography is a technique of diagnostic imaging which uses a system of low-dose X-rays to examine the inside of the breasts. This is a medical test that consists of performing a breast radiography. When performing a mammogram, a mammography machine is used. specific equipment: the mammograph.
It is a medical equipment that is specifically designed to capture X-ray images with a high resolution to detect signs and irregularities in breast tissue. The design and the different parts of a mammography equipment allow a minimum dose of radiation to be used during the test, making it an effective, fast and safe examination.
Health professionals use this test to look for early signs of disease in breast tissue. Among them, breast cancer. The mammography test is called mammogram and its main purpose is to detect abnormalities such as tumors, cysts or microcalcifications in the breast. We analyze, below, what mammography consists of, how the mammogram works and its different parts.
Mammography: What is mammography and types of mammograms?
The use of the mammograph is used as a screening tool for early detection of breast cancer in womenA mammogram is used both in women who have no symptoms and to diagnose the presence of abnormalities in women who notice breast irregularities. A mammography examination or mammogram exposes the woman to a small dose of ionizing radiation to generate medical images of the inside of the breasts. We can differentiate between two types of mammography:
Screening mammography
A screening mammogram is performed in women who have no signs or symptoms of breast cancer. This type of mammography should be performed periodically in women from the age of 40 as a form of prevention. By means of this diagnostic test, it is possible to detect irregularities in the breast tissue, such as tumors, cysts or microcalcifications. Screening for breast disease at early stages, especially breast cancer, provides a range of advantages:
- Allows the identification of tumors before they are palpable. or present visible symptoms.
- Enables treatment to be initiated in the early stagesbefore the disease has spread.
According to different studies, it has been proven that the screening mammography screening decreases breast cancer morbidity rates by detecting the disease at treatable stages, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
2. Diagnostic mammography
Diagnostic mammography is used when a woman presents symptomsas lumps, pain, discharge or changes in the skin of the breast. It is also used when an abnormality is detected on a screening mammogram or detection. This type of examination allows the affected area to be studied in greater detail and thus identify whether the breast condition is benign or malignant.
Mammograph operation
The medical equipment The mammogram is a specialized medical device that allows the analysis of breast tissue and the presence of abnormalities. This is specialized medical equipment that uses X-rays to generate medical images of the inside of the breasts. How a mammogram works consists of several stages:
Preparation of the patient
The process begins with the positioning of the patient in front of the mammograph. During the mammogram, a radiology professional will positions the breast on a flat platform of the mammography equipmentwhere the breast will be gradually compressed. The specialized technician will guide the patient to ensure proper posture and perform the medical test.
2. Breast compression
Once the breast is positioned, an adjustable compressor descends to press on the breast tissue gently, but firmly.
3. X-ray emission
The tube of X-rays of the mammogram emits a controlled beam of radiation passing through compressed breast tissue. This radiation is absorbed to a greater or lesser extent depending on the density of the tissue:
- The dense tissuessuch as tumors or microcalcifications, absorb more radiation. They appear clearer and brighter in the images.
- On the other hand, the fatty tissues absorb less radiation and appear darker.
4. Image capture
The radiation passing through the breast is captured by a detector which transforms the data into a digital image or radiographic film. Modern mammographs are often equipped with digital technology that allows images to be stored and processed on a computer.
Subsequently, these generated medical images can be integrated in the RIS system to automate the management of medical imaging data and information, facilitating its analysis and comparison with previous studies.
5. Variation of angles and views
To ensure a complete evaluation of the breast tissue, images are captured from different angles. The different perspectives help physicians identify abnormalities that may not be visible in a single view. The views that are analyzed in a mammography study are:
- Craniocaudal (CC)This is a top-down view.
- Mediolateral oblique (MLO)This type of slanted view allows a greater amount of breast tissue to be studied, especially that close to the axilla.
6. Image analysis
Once the images have been obtained, a specialized radiologist reviews the results for possible abnormalitiesas cysts, calcifications, tumors or suspicious tissue changes. Nowadays, digital images offer many advantages, since they allow adjusting contrast and brightness to improve image quality, obtaining a more efficient and accurate diagnosis.
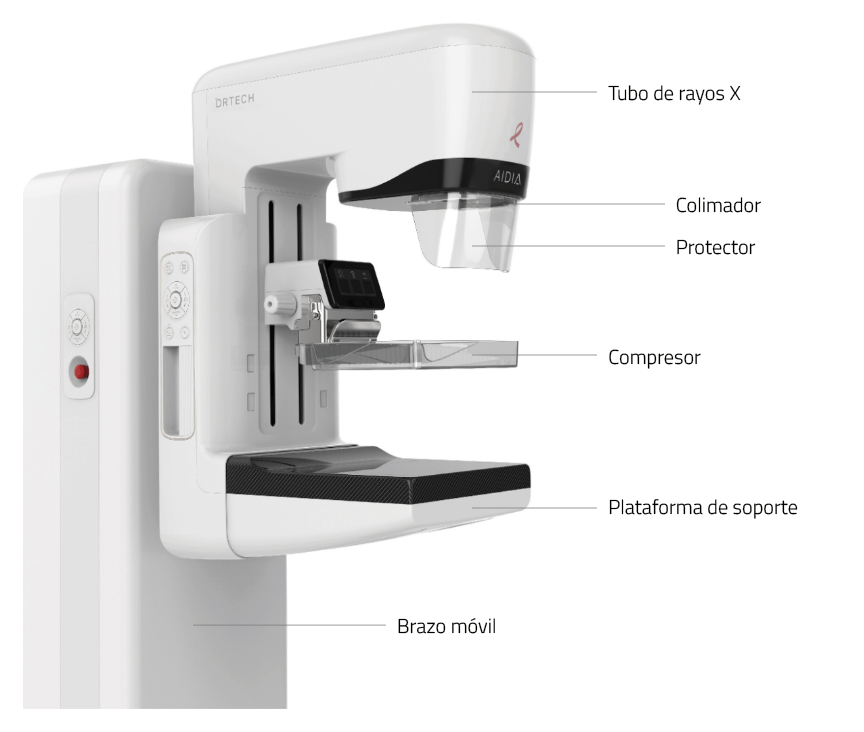
The mammograph: Parts and components
A mammogram is composed of several elements that work together to ensure clear and accurate images. Each component has a specific function that contributes to the quality of the diagnosis and the safety of the procedure. What are the main parts of a mammography machine?
X-ray tube
The X-ray tube is the component responsible for generating the X-ray beam that passes through the breast tissue. and subsequently produce high quality images. The mammograph uses a lower radiation doses than standard X-rays. This is because, since x-rays do not pass through this area easily, the mammography equipment is designed with two plates that compress and flatten the breast to separate the breast tissue. In this way, a higher quality medical image can be created and the amount of radiation during the exam can be reduced.
2. Compressor
The compressor is a movable plate that descends to press the breast against the mammography platform. Its function is to compress the breast tissue gently and firmly, providing the following advantages:
- Reducing the thickness of breast tissue to improve the visualization of internal structures.
- Minimizing X-ray scatteringThe image quality is improved.
- Avoid blurred images caused by the involuntary movement of the patient.
- Allowing the use of a lower dose of radiationmaking the procedure safer.
3. Support platform
The support platform is a flat surface on which the breast is positioned during mammography. It provides a stable and firm foothold, ensuring that the breast tissue is correctly positioned for sharp, detailed images.
4. Detector
The detector is the component that captures the radiation passing through the breast tissue and converts it into an image.. Depending on the type of mammograph, it can be of different types:
- DigitalX-ray: Converts X-rays into electronic data that is processed and stored in a computer, facilitating detailed and rapid analysis.
- Radiographic filmThis type of detector is used in analog mammographs, where the image is printed on a special film.
5. Collimator
The collimator is a structure that directs and confines the X-ray beam to the specific area of the breast that needs to be examined. This component prevents other areas of the body from receiving unnecessary radiation, making the procedure safer.
6. High voltage generator
The high-voltage generator is responsible for supplying the energy necessary for the X-ray tube to function correctly. It regulates the intensity and duration of the X-rays, adapting to the needs of each scan.
7. Control station
The control station is the panel or computer from which the technician operates the mammography machine. Allows you to adjust the parameters of the examinationIt also ensures that the procedure is performed in a precise and customized manner for each patient. It also ensures that the procedure is performed accurately and customized for each patient.
8. Positioning system
The positioning system includes mechanisms for adjusting the height, tilt and angle of the mammography machineThe system can be adapted to the physical characteristics of each patient. This system facilitates the imaging from different perspectivesobtaining a complete analysis of the breast tissue.
9. Image processing software
In digital mammographs, the digital mammogram processing software medical images is an advanced tool that improves the quality of captured images. Allows adjustment of contrast, brightness and other parameters to highlight specific details, as well as compare current images with previous studies, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis.
10. Security system
The mammogram is equipped with a safety system that ensures that radiation exposure is minimized and safe for the patient. In addition, some devices are equipped with sensors that automatically stop the process if a problem is detected technical or positioning.
Advantages of mammography
The mammograph is an essential medical device for the detection, diagnosis and follow-up of breast diseases, especially breast cancer. Its use not only allows early identification of abnormalities, but also contributes to more effective treatment planning. What are its main advantages?
Prevention and early detection of diseases
The mammograph is capable of identify abnormalities in breast tissue in early stages or even before symptoms and signs are visible. The early detection is key to significantly increasing the chances of successful treatment, as it allows the disease to be addressed before it develops to an advanced stage.
In turn, the periodic mammograms are performed is a fundamental strategy for the prevention of breast cancer in women. By detecting breast cancer in its early stages, it helps to reduce the mortality associated with this disease and improves the quality of life of patients.
Non-invasive, fast and safe procedure
Mammography is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses a minimal dose of X-rays, meeting strict safety standards. The mammography exam is fast and efficient. It usually has a duration between 10 and 30 minutesdepending on the type of mammography performed:
- The screening mammogramsDuration: Its duration is between 10 and 20 minutes.
- The diagnostic mammogramsThey have a longer life, between 15 and 30 minutesThey include different views and images to analyze the area in a specific way.
High precision imaging
Modern mammographs, especially digital mammographs and those using 3D technology (tomosynthesis), provide high-resolution images that allow the breast tissue to be analyzed in great detail. This precision facilitates the detection of small or subtle irregularities and improves the differentiation between normal tissues and abnormalitiesreducing the probability of false positives or negatives.
Examination customization
The design of the mammograph allows tailoring the procedure to the individual characteristics of each patient. Exposure parameters, X-ray intensity, acquisition angle and compression level can all be adjusted. All this allows you to generate high quality medical images and optimize the patient experience.
Fast and efficient diagnostics
The mammogram streamlines the diagnostic process by generate medical images in a short period of time. In this way, when abnormalities are detected, physicians can immediately plan further studies and start treatment as soon as possible.
Multiple uses and clinical applications
In addition to being a key tool for the early detection of breast cancer, the mammogram has also other important applications:
- Monitoring of the evolution of oncological treatments.
- Performing image-guided biopsiesThis improves the accuracy of the procedure.
- Identification of benign changes or non-malignant disease in the breast tissue.
Conclusion
The mammograph is an advanced technological tool that combines precision, safety and efficiency for the detection and diagnosis of breast diseases.
If you need advice on radiodiagnostic medical equipment, at 4D we help you choose the most appropriate solution that suits your clinic's needs and budget. We have new and second hand equipment, as well as renting and leasing options. Contact us without obligation.
Contact 4D
Bibliography
American Cancer Society (n.d.).
Mammogram basics. Retrieved January 15, 2025, from
https://www.cancer.org/es/cancer/tipos/cancer-de-seno/pruebas-de-deteccion-y-deteccion-temprana-del-cancer-de-seno/mamogramas/conceptos-basicos-del-mamograma.html
RadiologyInfo.org (n.d.). Mammography. Retrieved January 15, 2025, from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/es/info/mammo
MedlinePlus (n.d.). Mammography. U.S. National Library of Medicine Retrieved January 15, 2025, from. https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/mammography.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (n.d.). Mammograms. Retrieved January 15, 2025, from https://www.cdc.gov/breast-cancer/es/about/mammograms.html
Revista Argentina de Mastología (2020). Importance of mammography in the early detection of breast cancer. Retrieved January 15, 2025, from https://www.revistasamas.org.ar/revistas/2020_v39_n141/06.pdf
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.


por Kiko Ramos | Jan 9, 2025 | Projects
4D Medica has collaborated with the Hospital Clínico Veterinario CEU on the diagnostic imaging area. To this end, it has provided both the sale of different equipment like support, installation and maintenance of supplied medical equipment. The CEU Hospital is specialized in the area of Small Animals and Large Animals, so the cooperation with 4D Medica is a revolution in the clinical and research activity of the veterinary sector.
The CEU Clinical Veterinary Hospital, a reference center in the Valencian Community
The CEU Clinical Veterinary Hospitallocated in Valencia, has more than 20 years of experience in the veterinary field. This is in addition to the specialization of the medical team, new facilities, research and state-of-the-art technology. All these aspects have turned it into a reference center in the Valencian Community.
At June 2016was inaugurated on new Clinical Veterinary Hospital for Companion Animals and Large Animals at CEUof the Cardenal Herrera University. The center was built in a new facility with a total surface area of 4,536 square meterswhere they are housed diverse areas of expertise and spaces for clinical practice and research. Another aspect for which it stands out is that it is equipped with infectious animal isolation unitsbeing the first hospital in Spain that incorporates them.
The three pillars of the center
CEU Hospital focuses on three main pillars:
- TeachingAt the hospital, undergraduate and postgraduate students of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine of the CEU Cardenal Herrera University carry out their internships, and continuous training is provided to health professors. The Faculty is a member of EAEVE (European Association of Establishments for Veterinary Education), an entity that brings together the best Veterinary Faculties in Europe.
- ClinicalThe center is a referral center for owners and veterinary professionals who refer the diagnosis and treatment of complex cases.
- ResearchResearch activities, both internal and in collaboration with external entities.
Multidisciplinary referral service
It offers a multidisciplinary referral service with qualified specialists with experience in national and international hospitals. The hospital is open 24 hours a day, 365 days a year to attend to veterinary emergencies, prioritizing a quality medical care.
Medical equipment and technology in the area of Diagnostic Imaging, provided by 4D Medica.
It is a center that incorporates the latest technology in Hospitalization and ICU Units. With the 4D Medica collaboration and the medical equipment provided in the area of Diagnostic Imaging, has become a pioneer and reference hospital in the veterinary sector. For this purpose, it has audiovisual and information systems that facilitate the transmission of operations from the operating rooms and a data processing center which manages information in real time, connected to the university network.
New Large Animals area
The new facilities are equipped with the clinical care services for large animals, especially equines. It is, therefore, in the largest equine hospital in the Valencian Community. The diagnostic services offered are digital radiology, ultrasonography and video endoscopyamong other techniques. Regarding the type of health care, within the area of large animals, the following are carried out emergency, general medicine, specialized internal medicine, surgery and anesthesia clinical services.
Medical equipment and services supplied by 4D Medica
In the cooperation between 4D Medica and the Hospital Clínico Veterinario CEU in the area of Diagnostic Imaging, the following medical equipment was supplied:
Digital X-ray detector Vivix V-2430VW (2018)

During 2018, 4D Medica provided the detector of X-ray panel Vivix V-2430VW. It is a digital flat-panel detector of X-raysdesigned for general radiography applications. It is part of the Vieworks VIVIX-S V series, recognized for its advanced technology and robust design. Among its main features, we can highlight the following elements:
- Superior image qualityWith a pixel size of 124 µm, it offers a high spatial resolution of 4.0 line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm), capturing sharp, detailed images with minimal noise, enabling more reliable and accurate diagnoses.
- Ergonomic, lightweight and durable designThe detector is easy to maneuver and lightweight, making it comfortable to use for radiology technologists. In addition, it has built-in handles for easy carrying. At the same time, its glass-free design makes the detector resistant to shocks and drops, ensuring a long-lasting investment. In addition, it has an IP67 rating, which means it is dust and water resistant.
- Prolonged autonomyVIVIX-S 2430VW batteries last up to 16 hours on a single charge, allowing for intensive use without interruption. It supports a variety of charging methods, including wired charging, wireless charging and charging via a docking station.
- Automatic Exposure Detection (AED)Vieworks' patented Automatic Exposure Detection (AED) technology ensures that images are captured at the appropriate radiation dose for each patient, optimizing safety and comfort.
Sonosite M-Turbo, Sonosite Edge II, Wisonic Piloter and SIUI Ultrasound Scanners (2019-2024)
From 2019 to 2024, different models have been supplied and types of ultrasound scanners for accurate and quality diagnostic imaging.
Source || Freepik
Sonosite M-Turbo
It is a portable ultrasound scanner that is recognized for its durability and reliability. Weighs approximately 3.4 kg with batteryThis makes it easy to transport. It is designed for demanding environmentsIt offers a wide range of products and services, meeting U.S. military specifications. advanced image quality and turns on in less than 20 secondsIt can be used immediately. It is used in various diagnostic applications and clinical procedures around the world. From remote hospitals to veterinary clinics and community health centers.
Meet our medical team
Sonosite Edge II Ultrasound Scanner
This portable ultrasound system provides an enhanced imaging experience, while maintaining the same high quality of the images. design pillars: durability, reliability and user-friendliness. It has a wide-angle screen with an anti-reflective coating and has a simplified interface with a tactical panel with selection button that provides efficient navigation. At the same time, its silicone keyboard is sealed to prevent the entry of liquids and to allow adequate disinfection. On the other hand, it is ready to scan in less than 25 seconds and is suitable for various clinical applications.
Meet our medical team
Wisonic Piloter
It is a extremely lightweight tablet ultrasound scanner and with a weight of only 2 kg. It has a 13.3-inch touch screen that allows horizontal and vertical viewing. Through its extremely lightweight housing, intelligent design and built-in customized workflow, Piloter provides a more efficient experience for the user. musculoskeletal control, pain management, physical therapy and vascular system. Includes the wiNeedle technology for improved needle visualization during interventional procedures.
Meet our medical team
SIUI
The SIUI brand offers a variety of portable ultrasound scanners and with support for various clinical applications. For example, the Apogee 5300 Pro model is prominent in cardiology and radiology, offering advanced informatics capabilities that enable automated measurements essential for diagnosis. These devices are designed to provide a satisfactory image quality and intelligent applications that enhance diagnostic quality.
Portable X-ray generator MEX-20 (2022)
In 2022, the CEU Clinical Veterinary Hospital was awarded the MEX-20 portable X-ray generator. It is a portable high frequency X-ray generator, specifically designed for veterinary applications, especially in equine. It has the following components:
- Power and performancePower rating of 1.6 kW, equivalent to 4 kW in conventional systems, with a range of 50-90 kV adjustable in 1 kV increments, and a current of 20 mA.
- PortabilityNet weight of approximately 6.8 kg (including battery), it is easily transportable, facilitating its use in different clinical and field environments.
- AutonomyThe system is equipped with a high capacity battery (1600 mAs), which allows up to 160 exposures at 80 kV/10 mA on a single charge. Recharging time is less than 3 hours, ensuring continuous operation.
- Ease of useIt has an intuitive touch screen for parameter settings and has a memory for storing up to 10 presets. In addition, it has a dual laser pointer that facilitates precise positioning.
- Included accessoriesThe equipment includes a remote control and a portable case, providing protection and ease of transport.
Maintenance and repair of conventional small animal X-ray and endoscopy room (2017-2024).
Since 2017, in addition to the medical equipment provided, there have also been. maintenance and repair services for conventional X-ray room equipment of small animals and endoscopy.
Radiological image storage PACS, with 4D Medica installation and maintenance (2019-2024).

Source || Freepik
Technology is a key aspect that fosters better management of medical information and images. Beginning in 2019, 4D Medica included the PACS system in the radiology area of the Hospital Clínico Veterinario CEU. This is a computerized image archiving and communication system which is used in the radiology area to store and manage reports and medical images electronically. With this, the hospital has a data processing center that manages data in real time and is connected to the university network.
Conclusion
Through this project, 4D Medica and the Hospital Clínico Veterinario CEU have driven the medical innovation and cutting-edge technology in the field of diagnostic imaging. This has allowed us to provide a quality clinical service, teaching and research, becoming a pioneering and widely recognized veterinary center in the Valencian Community.
Bibliography
CEU Cardenal Herrera University (n.d.). Presentation of the CEU Clinical Veterinary Hospital. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from
https://www.uchceu.es/hospital-clinico-veterinario/conocenos/presentacion
Sonosite (n.d.). M-Turbo: Portable ultrasound system. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from. https://www.sonosite.com/la/products/sonosite-m-turbo
Sonosite (n.d.). Edge II: Portable ultrasound system. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from. https://www.sonosite.com/es/products/sonosite-edge-ii
Wisonic (n.d.). Sample Page - Wisonic Spain. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from https://wisonic.es/index.php/sample-page/
SIUI (n.d.). SIUI products for diagnostic imaging. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from. https://www.siuivet.com/
Vieworks (n.d.). VIVIX-S 2430VW: Digital X-ray detector. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from. https://xrayimaging.vieworks.com/es/detector/radiography/1231
4D Medica. (n.d.). Mex20HF Plus portable RX Mex20HF Plus equipment. Retrieved January 9, 2025, from https://www.4dmedica.com/equipo-rx-mex20hf-plus-portatil-p-1-50-1722/
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Medica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.