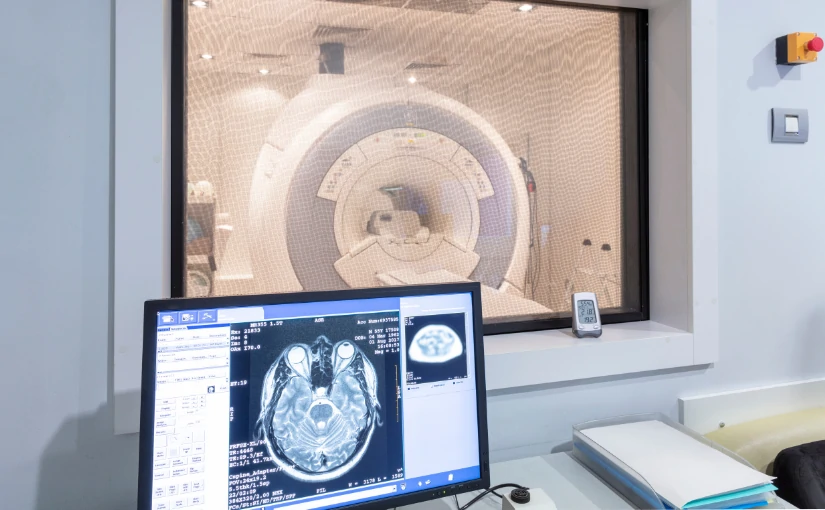
The interventional radiology (IR) is a specialized branch of the radiology area that combines techniques of diagnostic imaging with minimally invasive therapeutic procedures to diagnose and treat different diseases. In contrast to traditional surgical procedures, which require large incisions and long recovery times, interventional radiology allows for treat diseases without the need for open surgery. In this way, it stands out as an innovative discipline that reduces risks, recovery time and postoperative complications.
In the last decades, interventional radiology has experienced a great growth with the development of new technological advances both in imaging techniques and in medical equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of patients. interventional radiology. In the following article, we analyze what it consists of, its different types, as well as its main advantages and disadvantages.
What is interventional radiology?
Interventional radiology uses a series of diagnostic imaging technologies to guide therapeutic procedures with a high precision. The main modalities used are the following X-raysthe ultrasoundsthe computed tomography (CT) scans and the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
These techniques offer detailed information on the patient's anatomy and physiology in real timeThis allows medical professionals to visualize specific areas of anatomical structures and access them by making small incisions. To do so, they use specialized instruments such as catheters and needles. The use of high quality images and live viewing capability during procedures not only facilitates device placement, but also plays a key role in minimizing the risks associated with the procedure and reducing damage to healthy tissues.
IR is a medical discipline that is used for the treatment of treatment of various medical specialtiesThe company's main areas of expertise include oncology, cardiology, neurology, vascular radiology and musculoskeletal medicine. In turn, it has the capacity to offer less invasive procedures for patients who have certain risks in conventional surgery, such as the elderly, as well as patients with advanced pathologies or with a high surgical risk.
Interventional radiology procedures are performed under the following conditions local anesthesia, patients are awake during the procedure. Therefore, the risks that may arise from the application of general anesthesia are reduced. Another aspect to highlight is that most procedures are performed on an outpatient basis. In this way, patients can return home on the same day of surgery, reducing hospital costs and increasing the efficiency of the healthcare system.
The multiple advances in technology offer a great projection in interventional radiology. The integration of artificial intelligence in medicine and robotics has a special relevance in this discipline, which will increase precision and efficiency in the treatment of many diseases.
Types of interventional radiology
Medical technology continues to advance and interventional radiology plays a fundamental role in modern medicine. It is now used in different medical specialties and covers a wide range of therapeutic procedures. The main types of interventional radiology include vascular, oncology, musculoskeletal, gastrointestinal, urological, thoracic and gynecological, which we discuss below:
Guided image diagnosis
One of the main functions of interventional radiology is the diagnosis of diseases through image-guided procedures. In many cases, it is necessary to take tissue samples or drain fluids accumulated in the body to obtain an accurate diagnosis. Through the use of imaging techniques, these procedures can be carried out with a millimetric precision and without the need for invasive surgery.
Main diagnostic procedures
- Image-guided biopsiesBiopsies: Fine needles are used to remove tissue samples from organs such as the liver, lungs, thyroid or prostate. These biopsies make it possible to detect diseases such as cancer in its early stages.
- Percutaneous drainageWhen there is fluid accumulation due to infection or inflammation, catheters are placed to remove it without the need for major surgery.
- Puncture and aspiration of cysts or massesUsing a needle guided by ultrasound or tomography, physicians can remove cysts or reduce pressure in areas with fluid accumulation.
2. Vascular and endovascular treatment
The diseases of the circulatory systemsuch as arteriosclerosis, aneurysms and varicose veins can be effectively treated with interventional radiology techniques. In these cases, physicians use catheters and guidewires for accessing blood vessels and perform procedures that improve circulation or prevent serious complications. These treatments offer a less invasive alternative to conventional surgery, reducing hospitalization times and improving patients' quality of life.
Main treatments
- Angioplasty and stentingIn patients with blocked arteries, a balloon is introduced through a catheter to widen the blood vessel. Subsequently, a stent, a small metal device that keeps the artery open and prevents future blockages, is placed.
- Aneurysm embolizationWhen aneurysms, dangerous dilatations of the arteries, arise, micro-spirals or embolizing materials can be introduced to reduce the risk of rupture.
- Treatment of varicose veins and vascular malformationsSclerotherapy techniques are used to close abnormal veins and improve circulation, eliminating aesthetic discomfort and associated circulatory problems.
Clinical applications
- Peripheral arterial disease.
- Cerebral and arterial aneurysms.
- Stroke, cerebrovascular accident.
- Varicose veins and venous malformations.
3. Interventional Oncology
In the field of oncology, interventional radiology has opened up new possibilities for the treatment of cancer. canceras it allows the localized destruction of tumorsThe impact on healthy tissues and its side effects are reduced. Therefore, interventional oncology represents an important effective and less aggressive alternative to surgery.
Procedures in interventional oncology
- Percutaneous tumor ablationRadiofrequency, microwave or cryotherapy techniques are used to destroy tumors in the liver, kidney, lung and other organs without the need for open surgery.
- Chemoembolization and radioembolizationChemotherapeutic drugs or radioactive particles are administered directly into the blood vessels that feed the tumor, reducing its size and preventing its growth.
- Placement of catheters and central venous accesses.In patients requiring prolonged chemotherapy treatments, venous ports are inserted to administer the drugs more comfortably and safely.
Clinical applications
- Liver, lung and kidney cancer.
- Bone and soft tissue tumors.
- Palliative treatment in oncology.
4. Traumatology and pain management
Interventional radiology procedures are also essential for the management of chronic pain and the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries. These procedures improve the quality of life for patients by reduce pain and restore joint function without the need to resort to open surgery.
Most common interventions
- Joint infiltrations and nerve blocksAnesthetic and anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into joints such as the knee, hip or spine to relieve pain caused by arthritis or other conditions.
- Cementoplasty (vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty)In this type of procedure, a bone cement is injected into fractured or osteoporosis-damaged vertebrae to reduce pain and improve spinal stability.
- Aspiration of calcifications and drainage of articular cystsCalcium deposits in tendons or fluid accumulated in joints are eliminated, improving the patient's mobility and reducing pain.
Clinical applications:
- Osteoporosis with vertebral fractures.
- Herniated discs and chronic low back pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
5. Gastroenterology and urology
IR can be used to treat diseases of the digestive and urinary tract.
- Placement of esophageal and biliary prosthesisStents are inserted in the esophagus, bile ducts or intestines to allow the passage of food or liquids in cases of obstructions caused by tumors.
- Percutaneous nephrostomyDrainage: A drainage tube is inserted into the kidney to decompress urinary obstruction in patients with kidney stones or tumors.
- Treatment of gastrointestinal bleedingEmbolization is used to stop bleeding from gastric ulcers or esophageal varices, avoiding emergency surgery.
Clinical applications in gastroenterology
- Esophageal, liver and pancreatic cancer.
- Hepatic cirrhosis with portal hypertension.
- Biliary obstructions and intestinal strictures.
Clinical applications in urology
- Urinary obstruction due to tumors or kidney stones.
- Varicocele and fertility problems.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
6. Pulmonary and thoracic interventional radiology.
This specialty allows the diagnosis and treatment of thoracic diseases without the need for invasive surgical procedures.
Main procedures
- CT-guided lung biopsyLung tissue sampling for cancer diagnosis.
- Pleural drainage and pleurodesisElimination of fluid in the pleural space in cases of pleural effusion.
- Embolization of pulmonary arteriovenous malformationsClosure of abnormal blood vessels in the lungs.
Clinical applications
- Lung cancer and pleural diseases.
- Recurrent pneumothorax.
- Pulmonary vascular malformations.
7. Gynecology and obstetrics
In this medical specialty, the following treatments can be performed gynecological pathologies and pregnancy complications with image-guided procedures.
Main procedures
- Uterine fibroid embolizationNon-surgical procedure that reduces the size of fibroids without removing the uterus.
- Treatment of postpartum hemorrhageUterine arteries are occluded to stop severe bleeding after delivery.
- Pelvic abscess drainageGynecological infections elimination with percutaneous catheters.
Clinical applications
- Uterine fibroids and abnormal bleeding.
- Severe postpartum hemorrhage.
- Pelvic abscesses due to infections.
Meet our 4D Medical equipment
Advantages of interventional radiology
Interventional radiology offers many advantages and has transformed the treatment of many diseases, offering safer, less invasive procedures with shorter recovery times.
Minimally invasive procedures: Less risk and greater precision
One of the major advantages of interventional radiology is that it allows treatments to be performed without the need for open surgery. Instead of making large incisions, it uses small punctures in the skin through which catheters, microneedles and specialized devices are introduced.
This results in less damage to surrounding tissuesthere is a reduced risk of postoperative infections and you get a reduction of bleeding and scar formationimproving the patient's recovery.
Shorter hospital stay and faster recovery time
Interventional radiology procedures, being less aggressive to the body, allow the patient to recover in less time compared to conventional surgery. Many of the procedures are ambulatoryThe patient returns home after the procedure and is then hospital stay is reduced.
Another aspect to highlight is that the simpler and less invasive interventions. In this way, the decreases the consumption of painkillers since postoperative pain is less. At the same time, the patient can return to his or her daily activities and work in a shorter time, since the recovery times are shorter.
Less need for general anesthesia
Unlike traditional surgeries, which usually require general anesthesia, interventional radiology procedures are performed with local anesthesia and light sedation. This minimizes anesthetic risksespecially in patients with chronic diseases or advanced age. In addition to reducing the risk of complications, interventional radiology offers safer procedures for patients with cardiac or respiratory problems.
Highly accurate and efficient diagnosis and treatment
Interventional radiology uses real-time imaging to guide the placement of needles, catheters and other medical devices with extreme precision. The use of techniques such as fluoroscopy, ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging offers different benefits:
- Helps reduce the margin of error in complex procedures.
- Increased success rate of oncology and vascular treatments.
- Reduces collateral damage in adjacent structures.
Alternative treatment for patients who are not surgical candidates
For many patients with advanced disease or high surgical risks, interventional radiology is the only viable treatment option. It is a alternative for people suffering from advanced diseaseshave severe comorbidities or for those who reject invasive surgical procedures.
Covers multiple medical specialties
Interventional radiology is not limited to a single medical specialty, but is also encompasses several areas. Therefore, it provides a versatile treatment for treating diseases in different organs and systems, since it its approach is multidisciplinary. In addition, it is a discipline that is constantly evolving, thus allowing the application of new applications and technological improvements.
Lower cost compared to traditional surgeries
Although some interventional radiology procedures may involve more expensive medical equipment, their total cost is lower than that of conventional surgery. Among the main factors that reduce its costs, we can highlight the following aspects:
- Reduced consumption of medical resources and hospitalization time.
- Medication is reduced administered to patients.
- Faster recovery.
Disadvantages of interventional radiology
Despite its many benefits, interventional radiology is not without its limitations and challenges. Although it represents a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery, there are factors that may limit its application or affect patient safety.
Limited availability and restricted access
One of the main challenges in interventional radiology is that not all hospitals and clinics have the necessary technology and trained specialists. to perform these procedures.
In rural areas or countries with fewer resources, patients may not have access to advanced imaging equipment or interventional radiologists, limiting the possibility of receiving these treatments. In these cases, patients will have to travel long distances to receive care, so many of them will have to opt for more invasive surgeries due to the unavailability of interventional radiology.
Another disadvantage is that not all health systems finance these procedures. and this may generate economic barriers that hinder access to this medical discipline.
Not all procedures are equally effective in the treatment of the disease.
Although interventional radiology offers effective solutions for many diseases, some procedures only control symptoms or slow disease progression, but do not completely eliminate the disease. Therefore, IR emerges as a temporary solution until the patient is able to undergo definitive treatment. On other occasions, some treatments must be repeated several times to increase its effectiveness.
Use of ionizing radiation in some procedures
Many interventional radiology procedures, especially those that utilize X-ray machines and fluoroscopy, expose the patient to ionizing radiation. Although the doses are usually low, repeated exposure may increase the risk to the patient.
What impact can it have on the patient? On the one hand, cumulative exposure over the years. could increase the risk of adverse effectsespecially in repeated procedures. In turn, in young patients or pregnant women, the risk-benefit ratio should be evaluated with caution.
Possible adverse effects and complications
Although interventional radiology is generally safer than surgery, it is not without risks and complications. As these are minimally invasive procedures, there is a possibility of adverse effects in certain patients:
- Hemorrhage at the puncture siteMay occur in procedures that require the insertion of catheters in arteries or veins.
- Allergic reactions to contrast mediumIn studies such as angiography and cholangiography, some patients may present severe allergic reactions to iodinated contrast material.
- Infection at the puncture siteAlthough less frequent than in conventional surgeries, there is still a risk of infection.
- Device migrationIn rare cases, a stent or embolization coil may dislodge and cause unwanted obstructions.
Recent discipline and limited availability of professionals
The success of interventional radiology depends largely on the skill and experience of the interventional radiologist. In contrast to traditional surgery, where surgeons have extensive experience, IR is a relatively new specialtyand, therefore, the availability of highly trained professionals is still limited.
Conclusion
Interventional radiology is a recent medical discipline that offers high precision, reducing the application of invasive treatments and open surgery. In recent years, it has had a great impact on modern medicine, improving the quality of life of patients and reducing postoperative complications, hospitalization times and health care costs.
Do you need more information about medical equipment? Contact us and from the 4D Médica team we will help you find the equipment that best suits the different needs of your clinic or medical center.
Bibliography
Lonjedo, E. (2019). Interventional radiology: as far as the image takes you. Annals (Reial Acadèmia de Medicina de la Comunitat Valenciana), (20). Retrieved from https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7710219