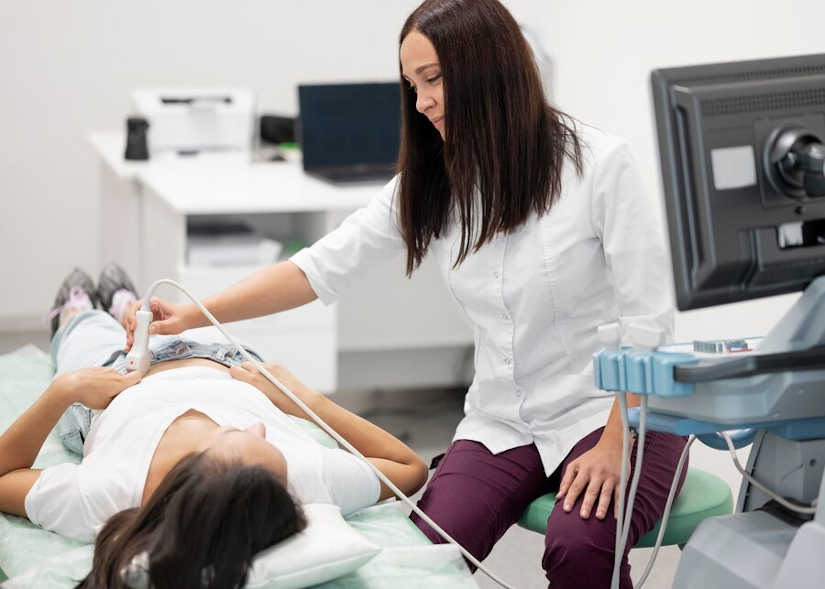
Ultrasoundultrasonography, also known as ultrasonography, is a non-invasive technique using ultrasound to obtain real-time images of the inside of the body. For this purpose, a medical equipment specific: the ultrasound scannerHow does it work and what types of ultrasound scanners are available on the market? We address this in the following article.
The ultrasound scanner: How does it work?
The ultrasound scanner is a medical equipment in the field of image diagnosis. It employs a device called a transducer which emits high-frequency sound waves, called ultrasound. These waves are inaudible to the human ear and travel through the different internal tissues of the body. At the moment when the waves encounter the various organs and structures, it is when are reflected as echoes. These echoes are picked up by the transducer and generate the medical images that can be displayed on a screen. These images are known as ultrasound scans and allow professionals to evaluate different tissues and internal organs of the organism.
In the realization of a ultrasoundis used, a transducer that glides over the skin in the area to be analyzed. This device is coated with a conductive gel that facilitates the transmission of ultrasound waves. It has the function of eliminating the air that exists between the skin and the transducer, helping to improve the quality of the images. In an ultrasound scan, the following can be obtained still images and also allows to observe the movement in real time. It is an essential medical equipment in medicine that has the function of analyzing the state of organs such as the heart or blood flow.
Meet our 4D Medical equipment
Parts of an ultrasound scanner
An ultrasound scanner consists of the following components:
| Parts of an ultrasound scanner | Description |
|---|---|
| Transducer or probe | Device in charge of emitting and receiving ultrasonic waves. |
| Monitor | Screen where the images generated by the ultrasound scanner are displayed. |
| Control panel | Interface with buttons and controls to adjust parameters and settings. |
| Central processing unit | Processor that handles the data and generates the ultrasonic images. |
| Storage system | Allows to save images and data obtained during diagnosis. |
| Power supply | Provides electrical power to the device. |
| Software | Program that controls the operation of the ultrasound scanner and processes the images. |
| Handles and wheels | Facilitate the mobility of the equipment within the hospital or clinic. |
| Ports and connections | They allow the connection of accessories and additional devices. |
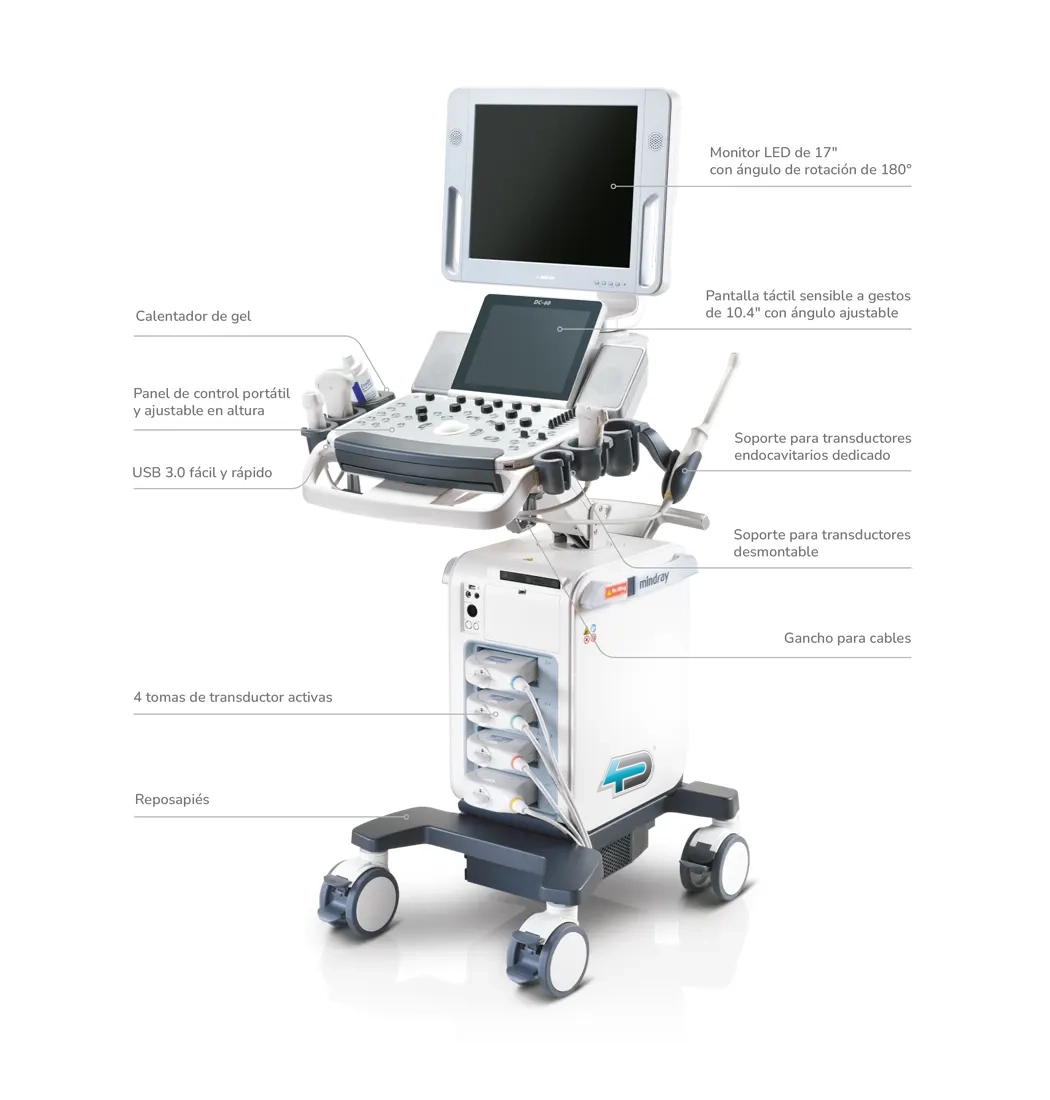
Detailed image of the parts of an ultrasound scanner
Transducer or probe
It is the main part of the device, responsible for transforming electrical signals into ultrasound waves. They are made of piezoelectric material and function as ultrasound emitters and receivers. There are different types of transducers:
Depending on its use
- LinearThey are used for superficial and vascular studies. They generate rectangular images and use high frequencies, since they do not require much penetration, being useful in the exploration of ligaments, tendons, muscles, thyroid, scrotum, breast and superficial vessels.
- Curved or convexThey have a curved shape and produce trapezoidal images. They are used with low frequencies because they are designed to explore deep structures, as in obstetrics and abdominal studies in general.
- Endocavitary or intracavitaryThey can be linear or convex. Their frequency varies according to the required penetration. They are used in intravaginal and intrarectal studies, for gynecological or prostate examinations.
- SectorialThey are a variant of the convex transducers and offer triangular or fan-shaped images. They use frequencies similar to those of curved transducers and allow an intercostal approach, so they are used in cardiac and abdominal studies.
According to frequency
- High frequency (up to 15 MHz)They are used to explore small and superficial structures.
- Low frequency (approximately 2.5 MHz)They are used for ultrasound scans that require a greater depth of penetration.
Monitor
Displays the images generated by the processing unit.The image is displayed on the monitor, so that professionals can observe and evaluate the state of the different anatomical structures in real time. Most current monitors can reproduce images in grayscale and color.
Control panel
It is located in the front part of the ultrasound scanner and allows the ultrasound specialist to make various adjustments to the equipment configuration. It allows to modify the brightness, the sharpness of the images and the frequency of the sound waves. In addition, it also allows to configure the necessary parameters to carry out the type of ultrasound that the patient requires.
Central processing unit
It is the component that receives the information provided by the probe. It converts the signals into electrical impulses and generates the image of the anatomical part of the area to be analyzed.
Storage system
It is the internal element that allows to save images and patient's data for further analysis. It can consist of an internal memory, USB or be connected to a PACS system (Picture Archiving and Communication System).
Power supply
Provides power to the ultrasound machineThe power supply is provided either by alternating current or by rechargeable batteries in the portable models.
Software
It is essential for processing ultrasound signals and generating medical images. It can include specific modules for different types of studies, such as cardiology or gynecology, among other areas.
Handles and wheels
These elements facilitate handling and transport of the equipmentespecially in the case of mobile ultrasound scanners.
Ports and connections
This type of components included in the ultrasound scanners are used for connect multiple probes, USB devices or DICOM interfaces to share images.
Types of ultrasound scanners
Having analyzed the operation of an ultrasound scanner and its main components, we can differentiate between different types of ultrasound scanners:
Imaging technology
1. 2D ultrasound scanners
- These are the most common and basic models. Generan two-dimensional images in real timeThey are widely used in the obstetrics area, to perform general and abdominal studies.
- Main applicationsBasic analysis, pregnancy control and organ evaluation.
2. 3D ultrasound scanners
- Allow display three-dimensional structures in real timeproviding greater detail. They are useful for creating more accurate images of fetuses and studying structural abnormalities.
- Main applicationsThey are used in advanced obstetrics and for surface studies of organs and tumors.
3. 4D ultrasound scanners
- They add the time dimension to 3D imagesallowing to see the movement in real time. It is especially useful in the obstetrics area to see fetal movements.
- Main applicationsObstetrical diagnosis and dynamic studies of joints.
4. Doppler ultrasound scanners
- They use the Doppler effect for assessing blood flow in vessels and organs. There are different models and variants:
- Color DopplerThey offer a color representation of the blood flow.
- Pulsed Doppler technologyThey provide a more detailed analysis of blood flow velocities.
- Continuous DopplerThey measure very fast flows.
- Main applicationsThey are used for vascular, cardiac and circulatory studies.
5. Tissue Doppler Ultrasound Scanners
- They are in charge of making a specific evaluation of the movements of the heart tissues and blood flow.
Mobility
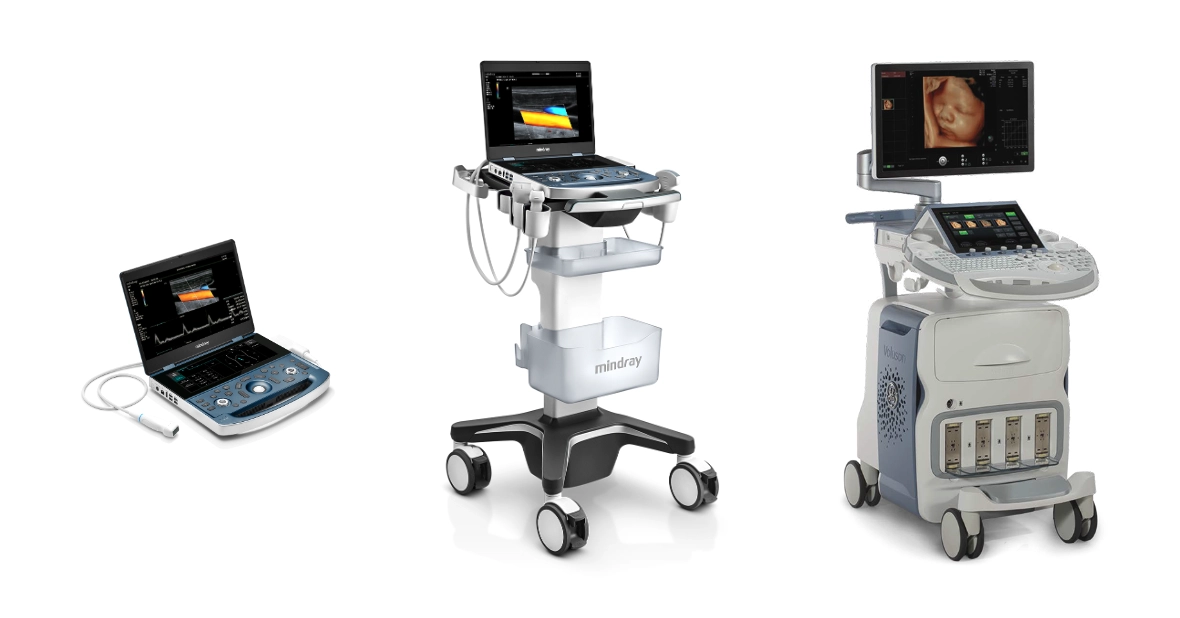
1. Portable ultrasound scanners
- They are small and lightweight devicesThey are ideal for home transport, emergency or remote areas. There are multiple versions that include advanced technologies, such as 2D ultrasound, Doppler, etc.
- Main applicationsThey are used for emergencies and ICU, mobile clinics and medical visits to remote areas.
2. Trolley or console ultrasound scanners
- They are larger and more robust models. They have a fixed console that offers a variety of functions and high-resolution imaging options.
- Main applicationsThey are used in hospitals and specialized clinics.
3. Wireless ultrasound scanners
- They are connected to mobile devicesThe medical imaging systems, such as tablets or smartphones, through applications. They are characterized by high portability and immediate access to the generated medical images.
- Main applicationsThey are used in sports medicine, emergencies and telemedicine.
Clinical Specialty
1. Obstetrics and gynecology
- This type of transvaginal ultrasound scanners are specialized in the visualization of the fetus, uterus and ovaries of women.
2. Cardiac (Echocardiograms)
- They are designed to evaluate the structure and heart function, valves and blood flow.
Vascular
- They are used for analize arteries and veinsmeasuring the flow and detecting obstructions or thrombi.
4. Musculoskeletal and Physical Therapy
- Allow visualizing muscles, ligaments, tendons and joints. These physiotherapy ultrasound scanners are used in sports medicine to detect injuries or to analyze the recovery from an injury.
5. Abdominals
- They are oriented to the study of abdominal organs like the liver, kidneys, spleen or pancreas.
6. Neurological
- They are used for assessing the brainespecially in neonates.
7. Urological
- These devices are designed to examine the kidneys, bladder and prostate of the male.
8. Endoscopic
- They combine ultrasound with endoscopes to obtain internal images of the digestive tract or areas of difficult access.
Resolution and advanced technology
1. High resolution
- This type of medical equipment offers images of the highest qualityIt is therefore especially useful in complex applications.
2. Ultrasound scanners with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Among the latest innovations, we can highlight the ultrasound scanners that incorporate artificial intelligence in medical image analysis. It has a technology that allows the automatic data and process analysis to offer a faster, more efficient and accurate diagnosis. At 4D Medicalwe are specialists in adapting the medical equipment software to the future of medicine.
Type of purchase
1. New ultrasound scanners
New ultrasound scanners are newly manufactured, previously unused ultrasound machines with the latest technology upgrades and full manufacturer's warranties. They feature the following characteristics:
- State-of-the-art technologyThey incorporate the latest innovations in imaging, such as advanced Doppler, elastography, 3D and 4D ultrasound and even artificial intelligence.
- Full warrantyThey offer extensive warranties that are backed by the manufacturer, generally from 1 to 5 years.
- CustomizationYou have the possibility to configure the equipment according to your specific needs, including transducers and software.
- Longer service lifeSince they have no previous use, their potential useful life is longer, especially if proper maintenance is carried out.
- Certifications and technical supportThey comply with all current quality and medical safety standards. In addition, they have specialized technical support.
2. Second-hand or opportunity ultrasound scanners
The used ultrasound scanners are previously used ultrasound devices that have been reconditioned or overhauled to ensure their functionality before being sold again. These devices may come from clinics, hospitals or doctors' offices that have refurbished them for newer models or no longer need them. Compared to new models, they have the following features characteristics:
- Technical reviewBefore being sold, ultrasound scanners undergo a series of quality tests to ensure that they are functioning properly. These may include repairs, cleaning, calibration and software upgrades.
- Reduced priceThey are less expensive than new equipment, which makes them attractive for small clinics, independent physicians or institutions with limited budgets.
- Variety of modelsYou can find from basic ultrasound scanners to advanced equipment with technologies such as Doppler or 3D.
- Limited WarrantySome suppliers offer warranties, but these are usually shorter than those for new equipment.
- Variable statusThe performance and service life of used ultrasound scanners will depend on how well the device has been maintained during previous use.
Conclusion
The ultrasound scanner is a medical equipment that is widely used in the field of diagnostic imaging to perform one of the most popular medical tests: ultrasound. Depending on the technology, mobility, medical specialty and type of purchase, different types of ultrasound scanners can be found.
There is a wide range of ultrasound scanners on the market that adapt to each of the medical needs. If you need more information, contact us and from 4D Médica we will offer you personalized advice so that you can choose the most suitable ultrasound scanner for your center.
Bibliography
MSD Manual (n. d.). Echocardiography and other ultrasound procedures. Retrieved from https://www.msdmanuals.com/es/hogar/breve-informaci%C3%B3n-trastornos-cardiovasculares/diagn%C3%B3stico-de-las-enfermedades-cardiovasculares/ecocardiograf%C3%ADa-y-otros-procedimientos-con-ultrasonidos#%C2%BFQu%C3%A9-es-una-ecocardiograf%C3%ADa?_v30149514_es
MedlinePlus (n. d.). Ultrasound. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/pruebas-de-laboratorio/ecografia/#:~:text=El%20ecografista%20utiliza%20un%20dispositivo,ondas%20sonoras%20en%20el%20cuerpo
Elsevier (n. d.). Ultrasound methodology and techniques: physical principles. Retrieved from https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-medicina-familia-semergen-40-articulo-metodologia-tecnicasecografia-principios-fisicos-13109445