por Kiko Ramos | Jun 16, 2025 | Projects
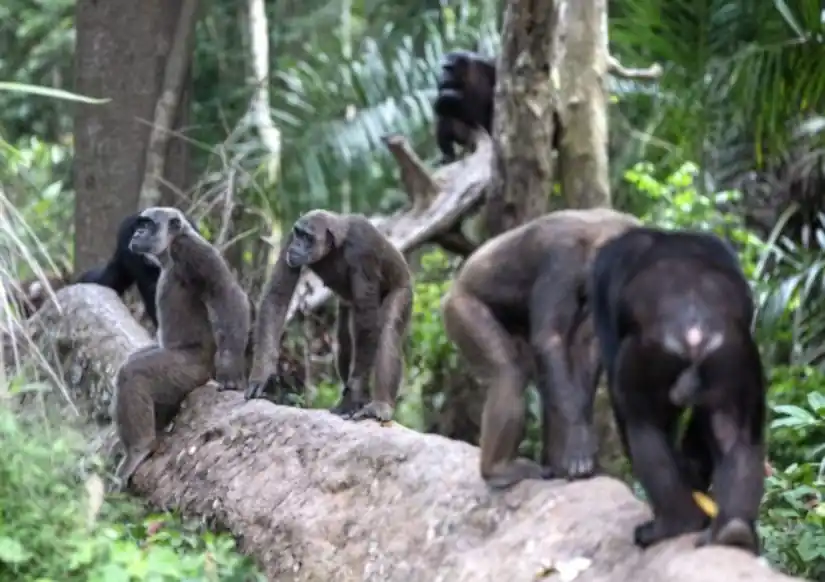
At 4D MedicaWe believe that innovation and medical technology must go where it is needed most. In our commitment to animal health, conservation and welfare, we have made an innovative collaboration with the Jane Goodall Institute. Specifically, with its Chimpanzee Rehabilitation Center of Tchimpounga (CRCT)located in the Republic of Congo.
Since its founding 30 years ago, the Jane Goodall Institute has had a key role in chimpanzee rescue and rehabilitation. Currently, this center represents the largest chimpanzee sanctuary in Africa. and is directed by Spanish veterinarian Rebeca Atencia. It is home to more than 140 orphaned chimpanzees rescued from illegal trafficking and poaching.
In this initiative, we have provided different medical equipment specialized with the objective of to promote better veterinary care. When the chimpanzees arrive at Tchimpounga, they are traumatized and require urgent veterinary assistance. In this area, medical technology is a fundamental resource to facilitate their rescue and rehabilitation process. And, subsequently, to give them the opportunity to be released back into their natural habitat.
Tchimpounga Chimpanzee Rehabilitation Center, the largest chimpanzee sanctuary in Africa.
Founded in 1992the Chimpanzee Rehabilitation Center of Tchimpounga (CRCT) is one of the world's leading centers for the rehabilitation of chimpanzees. Jane Goodall Institute's main initiatives in Africa. Located in the coastal region of Congo, the center was created in response to an alarming increase in illegal primate trafficking, which left hundreds of orphaned and traumatized offspring. It is located within the Tchimpounga Nature Reserve.which covers more than 520 km² and is home to wild chimpanzees and other endangered animals.
In the beginning, it started as a modest shelter, but has now evolved to become a international benchmark in chimpanzee rehabilitation. The center's mission is clear: to rescue, rehabilitate and offer a dignified life to chimpanzees that are victims of human exploitation.

A new paradigm in chimpanzee rehabilitation
In the 2010s, one of the most relevant milestones in the history of the center was its expansion into three river islands in the Kouilou River: Tchindzoulou, Ngombe and Tchibebe.. This initiative revolutionized the approach to chimpanzee rehabilitation. In this way, the animals were able to live in a more natural, safe and free environmentThey continued to receive veterinary support and monitoring from the Jane Goodall Institute team.
Why were the river islands of the Kouilou River chosen?
The three islands in the Kouilou River - Tchindzoulou, Ngombe and Tchibebe - were strategically chosen for several reasons:
- They are surrounded by waterThis prevents chimpanzees from escaping without the need for artificial fences.
- Rich in biodiversity and vegetationThis favors a semi-wild life with natural behaviors such as foraging, nest building and free play.
- Its location close to the main center facilitates access for veterinary staff and caretakers to supervise, care for and feed the chimpanzees when necessary.
Since their inception, these islands have become the most important final home of many rehabilitated chimpanzeesthat for various reasons (previous trauma, illness or age) cannot be reintroduced in total freedomThey can, however, enjoy a dignified, social existence in contact with nature. Currently, on the islands live in structured chimpanzee groups with stable social hierarchieswhere they can develop behaviors similar to those observed in the wild:
- They are fed of wild fruits, leaves and seeds.
- Free to move through the tropical rainforest.
- Form complex social bondswith games, alliances and hierarchies.
- They build nests in trees every night to sleep.
This model of semi-liberty has not only improved the quality of life of chimpanzees, but has also strengthened scientific research on their behavior in conditions close to their original habitat.

Medical technology at the service of animal welfare
As part of our collaboration with the Jane Goodall Institute, from 4D Medica we have provided medical equipment diagnostic imaging tailored to the specific needs of the Tchimpounga site. These tools help improve veterinary care in the following areas:
- Detect diseases respiratory, digestive or musculoskeletal disorders with greater precision.
- Perform non-invasive diagnostics to reduce stress in animals.
- Monitoring the evolution of chimpanzees recovering after trauma or infectious diseases.
- Planning surgical interventions or treatments more safely and efficiently.
Thanks to this technology, veterinarians can provide more comprehensive care, improving both the recovery rate and the quality of life of the animals throughout their rehabilitation process.
A road to freedom: The rehabilitation phases at Tchimpounga
The remediation process at the Tchimpounga Center aims not only to restore the chimpanzees' physical health, but also to heal their emotional traumas and reintegrate them into stable, natural communities. It is a complex and delicate process, designed to respect the rhythm of each animal, offering them a second chance at life. This process takes place in four fundamental phases:

1. Quarantine and intensive care phase
Upon arrival at the center, the chimpanzees go through a strict quarantine lasting at least 90 days. During this period, they receive complete and intensive veterinary care. Many of the animals arrive injured, malnourished or sick after being rescued from illegal trade or situations of mistreatment. Therefore, at the beginning, it is important to assess their general condition in order to stabilize and reassure them.
At this stage, the use of appropriate medical equipment is essential for an accurate diagnosis. to determine if there are injuries or illnesses and to plan the treatment to be followed in their rehabilitation.
2. Initial socialization and bonding phase
Once the quarantine is over, the youngest chimpanzees are integrated into living groups with other animals of similar age groups. It is at this time that they begin to acquire natural behaviors after contact with their peers and the support of specialized caregivers. It is therefore a fundamental stage in their development. social and emotional development.
3. Integration phase in stable communities
After a progressive adaptation phase, chimpanzees are introduced into stable social groups that mimic the natural dynamics of wild clans. These communities live in large forest enclosures within the sanctuarywhere they can move freely, climb, forage, establish hierarchies and form complex bonds.
4. Semi-freedom phase in the Tchimpounga Islands.
The final step of rehabilitation is the relocation of chimpanzees to the protected islands of the Kouilou riverwhich are part of the center's reserve. There, the chimpanzees can live in almost wild conditions, protected from human threatsbut with the necessary follow-up by the Jane Goodall Institute team. After this rehabilitation process, many of them fully recover their autonomy and have a second chance to live in an environment similar to their natural habitat.
Veterinary medical equipment supplied by 4D Medica
Through the contribution of veterinary medical equipment by 4D Medica, the Tchimpounga team has been able to further professionalize veterinary care in the rescue and rehabilitation process of the chimpanzees. This has boosted faster and more reliable diagnostics, safer and more efficient treatmentsas well as a precise monitoring of its evolution. The different devices supplied are described below:
Dry biochemistry equipment
It is a compact and efficient clinical analysis systemdesigned for environments with limited resources. By using this equipment, the following can be performed biochemical blood tests quickly and reliably, facilitating accurate field diagnostics.
Wireless digital X-ray detector Vivix-V2430
This medical equipment is a portable digital radiography detector. It has wireless connectionIt is suitable for environments where mobility plays a key role. It offers high-resolution images at high speedThe results of this study have been shown to improve the detection of fractures, bone anomalies or pulmonary problems.
Wired digital X-ray detector Vivix-V3543
Offers a robust high-resolution X-ray system and is designed for intensive clinical use. Its accuracy and integration capabilities make it a key tool for advanced veterinary diagnostics.
Sonosite M-Turbo portable ultrasound scanner
It is a high-performance portable ultrasound scanner. Among its main features, it stands out for its portability, durability and image quality in the field. It is used to perform minimally invasive abdominal, musculoskeletal and cardiac examinations.
Meet our medical team
Technology, commitment and conservation: A necessary alliance to achieve animal welfare
The collaboration between 4D Medica and the Jane Goodall Institute is an example of how technological innovation can be integrated with conservationcreating a real impact on the lives of animals. Every chimpanzee that walks freely in the forest again and every early diagnosis that saves a life is also part of our purpose.
Because, in the end, medicine not only treats bodies, it also repairs lives.
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Medica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.


por Kiko Ramos | Jun 3, 2025 | Projects
In the area of Diagnostic Imaging, technology plays a fundamental role in improving accuracy and efficiency in medical diagnosis. From X-ray machines, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment to ultrasound scanners and C-arms, the technology is playing a key role in improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnostics. investment in innovation and quality medical equipment is a key aspect.
At the same time, in order to provide quality health care, it is essential to provide a training complete health care personnel with the technical knowledge necessary for the correct use of Diagnostic Imaging equipment.. With this objective in mind, 4D Medica has initiated a collaboration with Monkole Hospital in the Congo.
The Monkole Hospital Center is located in Mont-Ngafula, a semi-urban area located south-west of Kinshasa, in the capital of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Through the Friends of Monkole Foundationan entity that collaborates with the hospital to promote the health service, we provide various medical equipment and specific training to healthcare personnelThe use of medical devices as well as the software installed.
Because we believe in the importance of cooperate and share technical knowledge where it is most needed. Especially in places like Congo, where resources are limited and the impact of technology can make a difference, helping to save lives.

Training of Monkole Hospital's technical staff in Diagnostic Imaging
Medical technology and innovation are constantly evolving. Every year new models of equipment are incorporated, improvements in imaging algorithms, integration with AI software and artificial intelligence systems, as well as new clinical and technical functionalities. For this reason, the training of technical personnel cannot be static and limited to initial training, but rather requires a ongoing training to improve the use of medical equipment and optimize technological resources in medical centers, clinics and hospitals.
To this end, in the collaboration with Monkole HospitalIn addition, we provided various medical imaging equipment and, in turn, we offered a technical training for its healthcare personnel. This center faces the daily challenge of keeping its systems operational without always having immediate technical support. Therefore, this is an initiative that not only seeks to improve the efficiency and durability of its diagnostic systems, but also to fostering local technical autonomy, This allows the hospital's own professionals to intervene more safely and quickly in the event of basic incidents. An action that, without a doubt, has a direct impact on the quality of health care offered to the population.
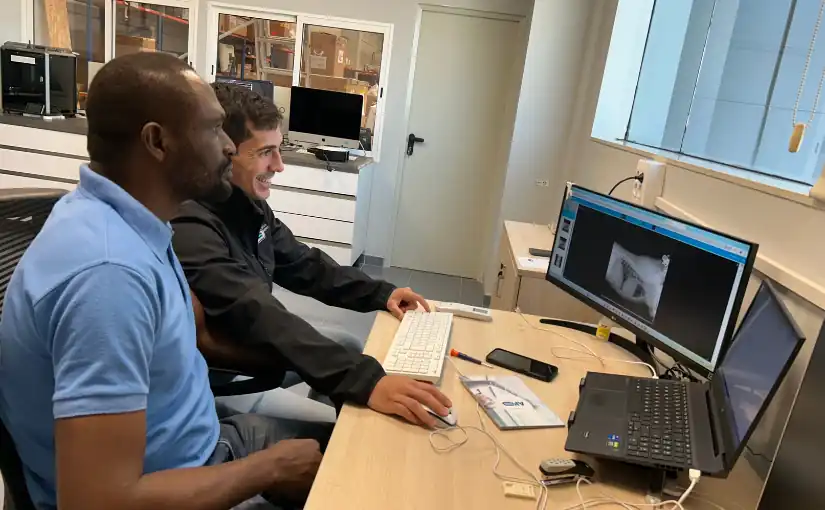
Monkole Hospital's technical staff visits 4D Medica headquarters
Healthcare technicians in charge of medical imaging devices play an essential role that goes beyond the basic operation of the equipment. As part of our efforts to provide training and technical expertise, we receive at the headquarters of 4D Medica to a health professional who is part of the technical team of the Monkole hospital center.. During your stay, our team offered you a comprehensive technical training on the use, basic maintenance and primary care of medical imaging equipment the center's facilities, as well as the installed medical software.
What are the advantages of a technical training in Diagnostic Imaging?
In this context, solid technical training improves healthcare and becomes a strategic factor in optimizing technological resources in a hospital center. In particular, we can highlight the following advantages:

Increased operating efficiency
Technical training enables healthcare professionals to use diagnostic imaging equipment correctly from the outset. This means a reduction in setup, acquisition and image processing times. Trained personnel not only know how to operate the equipment, but also how to choose the appropriate protocols according to each type of study, patient or clinical need. As a result, unnecessary delays and repetitions are minimized, improving the overall performance of the radiology service.
Improved diagnostic quality
A quality medical image is the basis for a good diagnosis.. Technical training provides key knowledge on parameters such as resolution, contrast, dose and patient positioning. A well-trained technician will know how to adjust these elements to to obtain sharper and higher quality images. This reduces errors of interpretation, avoids additional testing and improves the confidence of the medical team in the information it receives.
Prevent failures and breakdowns
One of the less visible, but most important benefits of training is the ability to identify and prevent failures before they become serious failures. Trained technical personnel know how to detect early warning signs, perform basic preventive maintenance tasks and apply restart or calibration protocols. This capability reduces dependence on external technical services and prevents equipment from being out of service for hours or days, affecting patient care.
Increased patient safety
Proper use of imaging equipment reduces risks associated with radiation exposure, dosing errors or poor patient positioning.. A well-trained technician not only protects the patient, but also protects himself and his environment. For example, they know when to use protective barriers, how to minimize the number of exposures needed, and how to act in the event of a technical emergency during a study. Safety is an essential part of the responsible use of medical technology.
Ability to adapt to new technologies
Technology in the field of diagnostic imaging advances rapidlysince the advent of hybrid equipment such as PET-CTto the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical image analysis. Continuous technical training enables personnel not only to adapt quickly to these changes, but also to take full advantage of them. A well-trained team facilitates the incorporation of new devices into the clinical workflow without interruption or error of the company's knowledge.
Increased technical autonomy in resource-constrained contexts
In hospitals in developing countries, access to specialized technical support may be limited or expensive. Training local staff in the basic operation and maintenance of diagnostic equipment is a key measure to ensure that the equipment can be used in a safe and efficient manner. long-term operability. This technical autonomy allows the center to maintain its active services without prolonged interruptions and improve your ability to respond to day-to-day failures.
Professional development of healthcare personnel
For healthcare technicians, training not only involves acquiring skills, but also growing professionally. Learning how to handle advanced technology, resolve technical incidents or collaborate in the implementation of new digital tools. enhances the team's commitment to their work and reinforces their role within the clinical environment.
Conclusion
In an increasingly technological healthcare environment, technical knowledge is as valuable as the use of quality medical equipment.. Technical training in Diagnostic Imaging not only improves the quality of healthcare, but also enables medical centers and hospitals to become more autonomous, efficient and sustainable.
From 4D Medica, we are committed to actions that integrate training, cooperation and sustainability as the axes of a more inclusive medical technologygenerating a real impact on people's lives.
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Medica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.


por Kiko Ramos | May 29, 2025 | Equipment analysis
Regulation of medical devices is an essential pillar in ensuring patient safety, medical efficacy and diagnostic quality throughout the healthcare system. All medical devices must meet stringent legal and technical requirements before they can be marketed and used in clinical practice.
In this context, the application of different measures and regulations for the regulation of medical equipment aims to protect users. And, at the same time, to bring confidence to healthcare professionals, transparency to manufacturing processes and traceability throughout the supply chain.
However, it is important to note that certifying a medical equipment is not just another administrative procedure. It is a multidisciplinary process ranging from design and clinical validation to the implementation of quality systems, risk management and post-marketing surveillance.
But what are the different regulations and processes that must be applied to market and use medical devices in clinical practice? In the following article, we provide a complete guide to the regulation of medical equipment and the current legal frameworks, both at national, European and international level.
What are medical devices?
The medical equipment is devices, apparatus or systems used in the prevention, diagnosis, treatment or rehabilitation of diseases and medical conditions. They range from simple medical devices such as syringes or thermometers to complex technologies such as medical equipment, such as magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound scannersremote monitoring systems or AI software of radiodiagnostics based on artificial intelligence.
Medical devices can be classified into different categories according to their level of risk for the patient and the user, which directly influences the type of regulation and certification that they must comply with.
Regulation of medical devices: The different regulations and processes
Regulation of medical devices varies from country to country or region to region, but in general, all medical devices are regulated in the United States. regulatory frameworks share a common goal: to ensure that the products are safe and effective for clinical use. Below, we review the different regulations and processes:
CE marking in the European context
In order to launch a medical device or medical equipment on the market and be marketed in the European Union, it must be CE marked. The CE marking is the legal requirement that authorizes the marketing of a medical device in the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA).
Indicates that the product complies with the provisions of Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on medical devices.the so-called MDR regulationsand can circulate freely within the European market. This regulation came into use in 2017 and replaced the previous Directive 93/42/EEC with the aim of strengthening the safety, traceability and post-market control of devices.
The first step in determining the CE marking process is to carry out the classification of medical equipment according to risk. Depending on the type of riskthe MDR standard defines a level of technical documentation and a regulatory process to ensure access to the European market. Specifically, medical devices are divided into four classes:
- Class ILow risk
- Class IIaModerate risk
- Class IIbHigh risk
- Class IIIVery high risk. Use of critical implantable/invasive devices
What does CE marking imply?
The CE marking is not a seal of quality, but rather a legal compliance indicator at European level. It guarantees that the manufacturer has followed a series of processes that certify the safety and efficacy of the medical device:
- Evaluation of the device according to the legal requirements of MDR regulations.
- The use of the medical device is safe and effective when used as directed.
- Implementation of a adequate quality management system.
- Use of post-marketing surveillance mechanisms and continuous clinical follow-up.
- Assessment by a Notified Body.
FDA Approval in the United States
In the United Statesthe Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the government agency responsible for the regulation, supervision and authorization of the marketing of medical devices.
It is developed through the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH)The FDA is an entity that ensures that all medical devices are safe, effective and manufactured according to quality standards before reaching the market. It classifies products into three categories:
- Class ILow risk, subject to general controls.
- Class IIModerate risk, require a 510(k) submission to demonstrate that they are substantially equivalent to another legally marketed device.
- Class IIIHigh risk. Require premarket approval (PMA) with detailed clinical evidence.
Key differences between FDA Approval and CE marking
| Appearance |
FDA (USA) |
EC (EU) |
| Scope |
United States and countries that recognize the FDA |
European Union and countries that accept CE marking |
| Target |
To authorize the marketing of medical devices under the direct supervision of the FDA. |
To certify that the product complies with the safety and performance requirements defined in the MDR Regulation. |
| Approach |
Stricter pre-market assessment |
Evaluation based on manufacturer's conformity |
| Clinical review |
PMA requires clinical trials |
Only Class III requires robust clinical evidence |
| Times |
Long, especially in PMA |
More agile in classes I and IIa |
| Evaluating Agency |
Public agency (FDA) |
Independent Notified Body |
Regulation of medical devices in Spain: The role of the AEMPS
At Spainthe Spanish Agency of Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) is the body responsible for applying national and European regulations on medical devices. Its main mission is to guarantee the quality, safety, efficacy and correct information of all medical devices marketed or used in the country.
The AEMPS under the Ministry of Health and acts as the competent authority to supervise compliance with Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on medical devices (MDR), as well as other national provisions. In Spain, the legal framework on the regulation of medical devices is articulated in terms of the following. regulations:
- Royal Decree 192/2023, which regulates medical devicesIt is the most recent and complete national regulation on medical devices. It aims to adapt Regulation (EU) 2017/745 to the Spanish legal system.
- Law 29/2006, on guarantees and rational use of medicines and health products.This Law is the general legal framework for everything related to medicines and medical devices in Spain. Although it was born focused on pharmaceuticals, it has been modified and extended to include medical devices.
- Technical guides and procedures issued by the AEMPS itself.The AEMPS regularly issues technical documents, instructions and guides that help manufacturers and economic agents to correctly interpret and comply with the standards.
ISO standards: Standardization and quality control in medical devices
The ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards are voluntary international standards that establish best practices for the design, production, evaluation and management of products and services.
In the medical devices field, are not a substitute for legislationsuch as MDR regulations in the European context or FDA approval in the United States. However, they are key instruments for demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and ensure the safety, efficacy and traceability of the product. The most relevant ISO standards are highlighted below:

ISO 13485:2016 - Quality management systems for medical devices.
It is the most important standard in this sector. It establishes the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) specifically tailored to medical device manufacturers and distributors.
Regulatory application
Not required by lawbut the implementation of an ISO 13485 system makes it easier to obtain CE markingIt reduces errors and demonstrates a commitment to quality and patient safety.
ISO 14971:2019 - Risk management for medical devices.
Establishes a structured framework for identifying, assessing, controlling and monitoring risk related to a medical device throughout its life cycle.
Regulatory application
It is mandatory in the context of the MDR to demonstrate that a thorough risk assessment has been performed. It is closely integrated with the technical documentation and clinical evaluation of the device.
ISO 10993 - Biological evaluation of medical devices
This set of standards addresses the biocompatible tests necessary to ensure that the materials in contact with the human body are non-toxic or provoke adverse reactions.
Regulatory application
These tests are mandatory for all devices that come into direct or indirect contact with the human body. Their compliance is part of the technical dossier submitted for CE marking or FDA approval.
ISO 14155: Human clinical trials of medical devices - Good clinical practice
Establishes the principles and requirements for the design, conduct, recording and presentation of clinical trials made in humans with medical devices.
Regulatory application
It is mandatory for manufacturers conducting prior clinical studies to CE or FDA certification, especially for class III or implantable devices.
ISO 62304: Software for medical devices - Software lifecycle processes
Defines the software development, maintenance and support requirements used as part of a medical device, or what constitutes a Software as a Medical Device (SaMD).
Regulatory application
As a result mandatory for any healthcare software that affects the diagnosis, treatment or monitoring of patients, either standalone or integrated in hardware. This is a key aspect in products such as medical apps, PACS systems or intelligent ultrasound scanners.
Conclusion
Patient safety starts with responsible certification. Regulatory applications are a key aspect of achieving responsible patient safety. safe and effective commercialization in the field of medical devices. Beyond a mere legal requirement, they represent a structured and rigorous process that ensures that medical devices have been designed, evaluated and manufactured under the most stringent quality standards. high standards of quality, safety and efficiency.
Whether under the CE marking framework in Europe, the FDA in the United States or national health authorities such as the AEMPS in Spain, evaluation and certification procedures are indispensable to ensure that technological innovation in the healthcare sector reaches the market in a responsible, efficient and sustainable manner.
Do you need medical equipment? In that case, do not hesitate to contact us and our 4D team will help you choose the best medical device according to the needs of your clinic or hospital.
Contact 4D
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.


por Kiko Ramos | May 8, 2025 | Projects
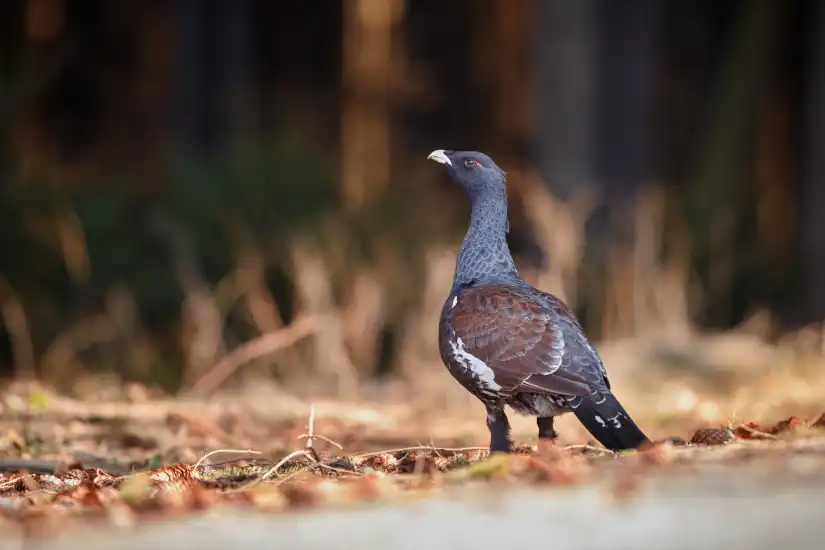
The cantabrian capercaillie is one of the most emblematic species of the peninsular biodiversity. With the aim of protecting and conserving this endangered species, an interpretation center for this bird and its natural habitat was created in 2006 in Caboalles de Arriba, in the municipality of Villablino de León. The Capercaillie Center is part of the network of Wild Animal Recovery Centers (CRAS) managed by the Natural Heritage Foundation of Castilla y León.
4D Medica has collaborated with the center through a public bidding process, contributing with medical equipment in the area of veterinary radiology. As experts in marketing and distribution of medical equipment, we have also carried out a collaboration with the CRAS in Burgos and Valladolid. In all these projects, 4D has supplied both X-ray equipment for veterinary medicine and protection materials for professionals. Below, we analyze the project, the work of the Capercaillie Center in León and the various medical equipment supplied.
Capercaillie Recovery Center in Leon
The Capercaillie Center is located in Caboalles de Arriba, in the municipality of Vallablino de León.and is part of of the Laciana Valley Biosphere Reserve, an area of high ecological value recognized by UNESCO. This area is home to species such as the The area is included in the Natura 2000 Network as a Special Protection Area for Birds (SPA).

What is the work of the Capercaillie Center?
The center is responsible for presenting the mixed oak forest ecosystem and one of its emblematic species: the Cantabrian capercaillie.. Seeks to provide a thematic exhibition The museum offers the recreation of a "cantadero", a place where the male grouse performs its courtship song, and allows the visitor to listen to the sounds of the forest through large windows that offer views of the natural environment.
In 2025, a new complete renovation of the exhibition with an investment of more than 400,000 euros, financed by FEDER funds and the Diputación de León. The objective is to communicate in a didactic and informative way the characteristics of the capercaillie habitat and the conservation efforts underway.
Featured species at the Capercaillie Center
The Capercaillie Center in Caboalles de Arriba (León) is an interpretation space dedicated to the conservation of the Cantabrian capercaillie and its habitat. In addition to the capercaillie, the center addresses other emblematic species of the Cantabrian Mountains:
- Cantabrian Capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus cantabricus)This is an endangered species and represents the symbol of the center. Aspects of its biology and behavior are presented, as well as the threats it faces.
- Cantabrian brown bear (Ursus arctos)Another emblematic species of the region is the brown bear, which is also in danger of extinction. Its ecological importance and conservation efforts are highlighted.
- Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus)It is a key predator in the Cantabrian ecosystems. The center offers information about its ecology and the role it plays in the natural balance.
- Other speciesThe center provides information on other species of local fauna, such as chamois, eagles and Egyptian vultures, which inhabit the forests and mountains of the area.

New Center for the Recovery of Wild Animals (CRAS) in Valsemana
Currently, the construction of a new Wild Animal Recovery Center at the Valsemana estatein the municipality of La Ercina, in León. This center, managed by the Junta de Castilla y León, will be located in a strategic enclave that already houses facilities such as the Capercaillie Breeding Center and the Brown Bear Acclimatization Center.
The creation of CRAS reinforces the commitment to wildlife protection and will provide opportunities for research and training in this area. This new CRAS joins the existing network in Castilla y León, which includes centers in Valladolid, Burgos and Segovia, and reception centers in Zamora and Salamanca. In 2024, these centers cared for more than 8,600 specimens, an increase of 22% over the previous year.
What will the new CRAS offer?
The new center will have specialized facilities for the treatment and rehabilitation of various wildlife species, including:
- Large carnivoresLike the brown bear and the Iberian wolf.
- MesomammalsMedium-sized mammals, such as foxes and badgers.
- Birds of preyEagles, owls and other protected bird species.
Valsemana's CRAS will also feature facilities for necropsies and cause of death studiescontributing to the research and conservation of wildlife in the region. Both centers play a crucial role in the conservation and recovery of endangered species in the Cantabrian Mountain RangeThe project offers environmental education and promotes the biodiversity of the area.
Medical equipment supplied by 4D Medica to the new Capercaillie Center
The recent investment in facilities, technology and medical equipment by the Junta de Castilla y León seeks to improve veterinary care and obtain a faster and more accurate diagnosis of the different species of fauna treated in the different centers. To achieve this, 4D Medica has collaborated with the new CRAS of Valsemana, contributing different equipment in the area of veterinary radiology:
Digiray's FireCR Spark X-ray imaging system
The FireCR Spark, developed by Digiray, is a digital X-ray reading system designed to provide high resolution images with great speed and flexibility. This equipment is specially designed to meet the demands of the clinical environment, both in human and veterinary medicine.
Main advantages and features
- Sharp and precise imagesIt incorporates an advanced signal capture technology that allows to obtain radiographs with a high level of detail, facilitating more accurate diagnoses.
- Compact and functional designIts light structure and small size allows it to be easily placed on surfaces or mounted on the wall, making the most of the space available in the office or clinic.
- Versatility in the use of cassettesThe FireCR Spark is compatible with different cassette sizes, adapting to a wide range of radiological studies.
- Tailor-made performanceAvailable in different reading speed configurations, allowing to choose the most suitable model according to the workload and the needs of the medical or veterinary center.
- QuantorMed+ software includedThe system is accompanied by QuantorMed+ Imaging software with an intuitive interface, fast processes and unlimited updates. This ensures that the system is always equipped with the latest features and technological improvements.
Meet our medical team
Unix4D X-ray equipment
The 32kW Unix4D equipment is a high-frequency X-ray system designed specifically for the veterinary environment. It combines power, precision and ease of use, offering an efficient tool for diagnostic imaging in animals.
Main advantages and features
- High frequency X-ray generatorWith an output power of 32 kW, it allows a voltage range of 40 to 125 kVp and a current of 25 to 500 mA, adapting to various diagnostic needs.
- Integrated X-ray tubeIt is equipped with a 3,000 RPM rotating anode and a 2.0 x 1.0 mm focal spot, ensuring high quality images.
- 10″ LCD touch screenEasy configuration and control of the equipment through an intuitive interface.
- APR anatomical programIncludes more than 300 pre-programmed anatomical views, optimizing workflow and reducing exposure time.
- Floating table with integrated buckyIt is designed to facilitate patient positioning by means of a self-supporting column and sensor-activated magnetic brakes.
- Manual calibrationIt allows precise adjustments to be made, adapting to the particularities of each study.
- Available configurationsThe Unix4D is available in different power ratings: 4, 8, 10, 12 and 32 kW, as well as in various mechanical configurations, allowing it to be adapted to the specific needs of each veterinary clinic.
Meet our medical team
Radiation protection equipment plumbed for veterinary use
The X-ray plummet protection equipment are designed to to protect veterinary professionals and auxiliaries from exposure to ionizing radiation. during the performance of radiographic studies on animals. This type of protection includes a variety of garments and accessories made of materials incorporating lead, specifically designed to block or reduce the penetration of lead. X-rays and thus protect the most vulnerable areas of the human body.
Although radiation doses in veterinary radiology are generally low, repeated exposure over time can lead to significant health risks for practitioners if appropriate radiation protection measures are not implemented. safety and radioprotection in clinical practice daily.
Meet our X-Ray protection accessories
Conclusion
With the contribution of these medical teams, we are promoting a improved veterinary care and diagnostic accuracyThe park has a key role in the protection and conservation of the various endangered species of the Cantabrian Mountains.
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Medica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.

por Kiko Ramos | Apr 30, 2025 | Equipment analysis
Computed radiographyalso known as CR (Computed Radiography), is a technique of image diagnosis which represents a transition between conventional radiology and current digital technologies. Instead of using traditional radiographic film, CR uses photoluminescent phosphor plates that store the energy of the X-rays. This energy is then released and converted into a digital image by a laser readout process.
This system makes it possible to digitize radiographic images without the need to completely transform the X-ray service infrastructure. It is therefore considered to be a intermediate solution between analog and direct digital technology (DR). It is especially useful in clinics or centers seeking to modernize their equipment without making investments as high as those required by DR. In turn, computed radiography can also be used to facilitates the storage, archiving, distribution and analysis of images in digital format. Therefore, the use of this diagnostic imaging technology provides a increased workflow efficiency in the medical environment.
In the following article, we discuss how computed radiography works and its workflow, its advantages and limitations, as well as its main uses in clinical practice.
Computed radiography: How does it work?
The operation of the RC is based on the use of reusable imaging plates coated with a phosphorous material that reacts to exposure with X-rays. This method combines laser technology, optical detection and digital processing in a single sequence.
As a result, by means of computed radiography, the following are obtained high quality diagnostic imaging without the need for chemical processes. The procedure consists of the following stages:

- Image captureFirst, the patient is positioned on the medical equipment to begin the scan. The X-ray exposure impacts on a CR plate, also called a cassette, where the energy is stored in the form of electrons trapped in phosphorous crystals.
- Plate readingAfter exposure, the cassette is inserted into a CR reader. This is a device that uses a laser beam to excite the electrons stored on the plate and then release the energy in the form of visible light.
- Conversion of light into digital imageThe light generated is captured by sensors (photomultipliers), which transform it into electrical signals. Using an analog-to-digital converter, these signals are converted into a digital image.
- Visualization and processingThe resulting image is displayed on a workstation, where different parameters can be adjusted. From modifying brightness, contrast and sharpness to adding annotations, measurements or labeling the image.
- Deletion of the plateAfter the process is completed, the plate is completely erased by intense light to remove any residual information. The process is then completed and the plate can be reused in another study.
Clinical workflow in computed radiography
The workflow in a computed radiography environment is systematic and designed to optimize time and ensure patient traceability. Although it is a more agile and efficient system than traditional development, it is not as immediate as direct digital radiology. Below are the different phases of the computed radiography workflow:
- Patient identification and study prescriptionIt starts with the loading of the patient's record in the RIS system (Radiology Information System), where the parameters of the request and the type of study required are defined.
- Image acquisitionThe technician positions the patient and makes the exposure with the CR plate in the cassette, as in a traditional X-ray.
- Digital reading of the cassetteAfter exposure, the cassette is transferred to the CR reader, where the latent image is digitized through the process described above.
- Processing and post-productionThe digital image is processed by specific software, allowing the technical parameters to be adjusted to optimize diagnostic visibility.
- Technical and medical validationThe technician checks the quality of the image before sending it to the radiologist, who will perform the clinical interpretation and generate the diagnostic report.
- Distribution and archiving: Finally, the image is stored in the PACS system (Picture Archiving and Communication System) and is included in the patient's electronic medical record.
Advantages of computed radiography
The adoption of computed radiography systems brings a number of important benefits to both healthcare personnel and medical facilities:
- Reduction in the use of chemicalsDoes not require the use of liquids or developer, which reduces environmental impact and biohazards.
- Reuse of platesPhosphor plates can be reused. Therefore, it offers great economic savings in the medium term.
- Improved image qualityCompared to analog radiology, CR offers better sharpness and digital adjustability.
- Easy integration into existing digital systemsIt can be connected to workstations such as the PACS system, the RIS system or DICOM printers, facilitating the exchange and management of medical information.
- Adaptability to existing equipment: Many installations of old X-rays Traditional or traditional systems can continue to be used with CR systems, which minimizes the initial costs of digitization.
Limitations compared to other techniques
Despite its advantages, computed radiography has certain limitations when compared to more advanced technologies, such as direct digital radiology (DR) systems:
- Increased processing timeThe technician must physically handle the cassette, which lengthens the time between exposure and image display.
- Increased operational burden for technical staffThe reading and handling of the cassettes involves additional steps that do not exist in the DR technique, where the image appears automatically.
- Slightly lower image qualityIn situations where maximum resolution and diagnostic accuracy is required, such as in fine lung studies or mammography, DR usually offers better results.
- Maintenance costs of CR readersAlthough CR technology is more affordable than DR, it requires a specific reader that involves maintenance, calibration and, in some cases, replacement of parts.
What are the differences between computed radiography (CR) and direct digital radiography (DR)?
| Features |
Computed Radiography (CR) |
Direct Digital Radiology (DR) |
| Image capture |
Requires cassette with phosphor plate |
Digital sensor integrated in the equipment |
| Image acquisition time |
Slow (requires scanning of the cassette) |
Immediate (real time image) |
| Equipment handling |
Manual intervention of the technician for each study |
Automated, requiring fewer steps |
| Image quality |
Good, but inferior to DR |
Excellent resolution and detail |
| Cost of implementation |
Moderate, reuses traditional equipment |
High, requires investment in advanced technology |
| Reuse of the detector |
Yes, with erasable phosphor plates |
Yes, with integrated digital sensors |
| Uses |
Centers with progressive transition to the digital environment |
High-demand, fast-flowing hospitals and clinics |
Our 4D Medical equipment
Main uses of computed radiography in clinical practice
Computed radiography (CR) is used both in medical centers, hospitals and clinics as in mobile units. It offers a wide versatility, has a low operating cost and provides high compatibility with conventional equipment. These are its main applications in clinical practice:
General radiology
It is used for routine studies such as X-rays of the chest, abdomen, spine, pelvis and extremities. It is an ideal technique for initial and follow-up examinations.
Emergency and traumatology
In emergency departments, CR allows rapid imaging of fractures, dislocations or bone injuries without the need for chemical processing. It is very useful in the rapid evaluation of polytraumatized patients.
Postoperative control
It is used to verify the correct placement of prostheses, screws or osteosynthesis material after orthopedic surgery, as well as for the evolutionary follow-up of injuries.
Thoracic and pulmonary evaluation
Chest radiography is one of the most frequent applications. It can detect infections, pleural effusions, nodules or signs of heart failure. CR facilitates digital contrast adjustment to improve the visualization of lung structures.
Dentistry and orthodontics
In some centers, computed dental radiography is used for orthopantomography, cephalometric studies or periapical radiographs, especially when compatible digital adapters are available.
Veterinary applications
Many veterinary centers use computed radiography as their primary imaging system because of its economy and ease of use, especially for radiographs of small and large animals.
Mobile units and health campaigns
Because of its portability and ease of installation, computed radiography is used in radiology trucks or mobile units.
Conclusion
Computed radiography is an effective, flexible and versatile medical technique. which has been key in the digitization process of diagnostic imaging services. It offers an efficient alternative for centers that wish to modernize without replacing all their equipment, adapting to multiple clinical environments.
Newer technologies, such as direct digital radiology, provide more automated and streamlined processes. Nevertheless, CR is still a viable alternative that can be used especially in small and medium-sized medical centers, mobile units or services with limited budgets that require a progressive transition to digital systems.
If your clinic needs advice on which computerized, conventional or direct radiography equipment is most suitable for your center, at 4D Médica we have the solution for each particular case. Request information without obligation.
Contact 4D Médica
Bibliography
Vergara E, Mauricio, Sepúlveda R, Gladys, & Vega T, Daniela (2006). RADIOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE IN COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY. Revista chilena de radiología, 12(4), 153-156. https://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0717-93082006000400003
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.