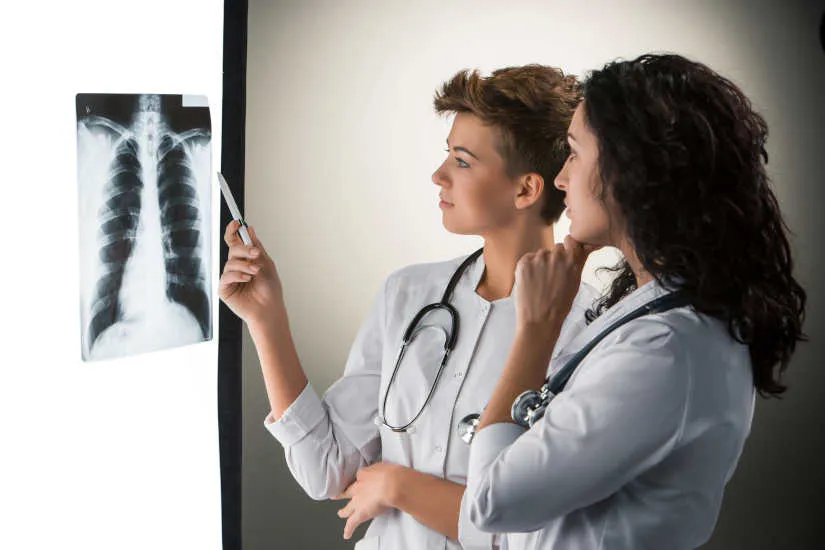
The X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, similar to visible light. This medical technique was created in 1895 by the physicist Wilhem Conrad Röntgen, whose findings led to the development of radiological practice. It is an essential method in the medical field and is used by means of specific equipment: the X-ray machines. X-rays are able to penetrate matter, so they can pass through most objects and tissues, including the human body. Once through the body, the X-rays reach a radiographic plate or computer where digital images, known as radiographs, are generated.
The radiographs are a type of diagnostic imaging and are used to analyze the different internal areas of the organism. The images that are produced are displayed in different shades of black and white.since each tissue allows a certain amount of X-ray beams to pass through it.. Dense materials, such as bones and metals, appear black, while muscles and fatty elements appear in shades of gray. In some types of X-rays, a contrast medium, such as iodine or barium, is introduced so that tissues can be visualized in the images in greater detail.
X-rays can be used aloneas in the equipment of conventional radiology, or combined with other techniquessuch as computed tomography or CT. In the following article, we explain how X-rays work, what they are used for and the types of X-ray machines that exist.
How do X-ray machines and X-rays work?
For imaging in conventional radiography, the patient stands behind a screen that blocks the radiation and operates the X-ray equipment. During the procedure, the body part to be analyzed is placed between the X-ray source and an X-ray detector.
The X-rays passing through the tissues are recorded on a radiation detector plate. Y, depending on the density of the tissues, will pass through a certain amount of radiation.The image produced shows the different degrees of density of the internal structures of the organism. The higher the tissue density, the more X-rays pass through and the whiter the image generated.How are the different tissues displayed?
- Metal has a white color.
- Bone see almost white.
- Fat, muscle and fluids are shown with shadows, in different shades of gray.
- Air and gas are displayed in black color.
Main uses of X-rays
X-rays have multiple uses in the field of medicine. X-rays are used for the diagnosis of diseases and injuries, as a support technique to perform surgical procedures, as a therapeutic treatment, in minimally invasive procedures and for the early detection of diseases. Below, we discuss the different procedures where X-ray technology is used to diagnose and treat diseases:
Diagnostic radiography
X-rays are used as diagnostic test to detect bone fractures, tumors and abnormal masses, pneumonia, etc.as well as lesions, calcifications, foreign objects, intestinal obstructions and dental problems.
2. CT or computed tomography
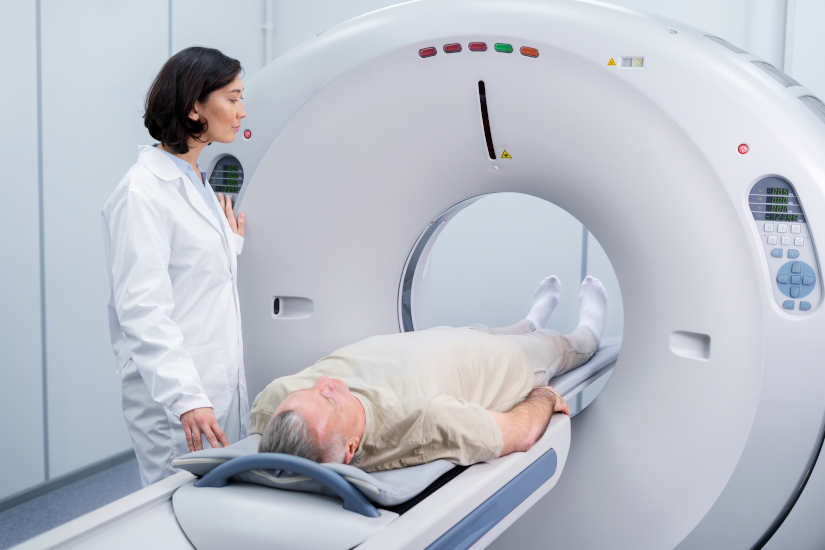
It combines the X-ray technique together with the computed tomography or CAT scan to create cross-sectional images of the body. Subsequently, can be combined to generate a three dimensional image X-ray images. CT images are more detailed than those of a conventional X-ray and allow professionals to analyze the internal structures of the body from various angles.
Mammography
Breast radiography is used to detecting breast disorders, mainly breast cancer. Breast tissue is sensitive to radiation, so special mammography units are used to minimize radiation exposure. digital radiology equipment.
4. Fluoroscopy
X-rays and a fluorescent screen are used together. to obtain real-time images of the movement inside the body. It is also used to analyze diagnostic processes, such as following the path of a contrast agent.
One of the uses of fluoroscopy is to analyze heart movement and beats. For this, radiographic contrast agents are used to view the blood flow in the heart muscle, blood vessels and organs. This type of technique is also used to guiding an internally threaded catheter during cardiac angioplastya minimally invasive procedure to open clogged arteries that supply blood to the heart.
5. Therapeutic use of radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer.
Another use of X-rays is as therapeutic technique to destroy tumors and cancer cells. The dose of radiation used to treat cancer is higher than the radiation used in diagnostic tests. This type of therapeutic radiation can come from X-ray equipment or radioactive material. that is placed in the body or bloodstream.
Types of X-ray machines
What types of X-ray machines are available on the market? We can differentiate the following medical equipment using this technology:
Conventional X-ray machines
They are the most basic equipment and are designed to obtain static images of the internal structures of the body. It is used for diagnose bone fractures, pulmonary evaluation by means of a chest X-ray and the identification of dental problems.
Portable X-ray machines
This type of X-ray machines are lightweight, compact and portableThe products can be easily transported. Used in emergencies and rural areasand to care for patients who cannot be transferred.
Digital X-ray machines
They are replacing film plates with digital detectors to develop a real-time diagnostics and the generated images have a high resolution and are of higher quality.
Fluoroscopy systems
These are specific devices that use X-ray technology for the following purposes observing dynamic processes in the body in real time. These machines are used for minimally invasive surgical procedures, gastrointestinal studies and orthopedic diagnostics.
Mammography machines
They are designed for perform breast tissue studies. They are essential for the screening for tumors, abnormalities and breast cancer. In this case, the X-ray emission is low energy in order to better analyze the soft tissues that make up the breasts.
Computed tomography or CT equipment
These units are designed with a advanced system that uses X-rays to create detailed, three-dimensional images of the body. It is highly accurate and is used to evaluate internal injuries, tumors, as well as brain, thoracic, abdominal and extremity studies.
C-arc
These X-ray machines are equipped with a C-shaped arm que emits the X-rays from one end and captures digital images at the other end. C-arc is used for image-guided surgical procedures and in orthopedic and cardiovascular interventions. It offers a deeper analysis, since the area to be analyzed can be visualized from different angles.
Dental X-ray machines
This type of device is designed for capture images of the teeth and various maxillofacial structures. On the one hand, there are the intraoral equipment which capture images of the inside of the mouth and, on the other hand, there are the extraoral equipment which include panoramic systems that take full images of the jaw and mouth. They are mainly used for the diagnosis of caries, periodontal diseases and orthodontic planning.
X-ray machines for bone densitometry
X-rays are used to measuring bone mineral densityand, therefore used to diagnose osteoporosis and perform the follow-up of bone loss treatment.
Meet our 4D Medical equipment
Conclusion
In conclusion, X-rays are a very complete technique that has a large number of uses in the health field and, depending on each medical need, there is specific X-ray equipment to analyze, study and treat various diseases.
If you are interested in purchase an X-ray machine for your clinic, health center or hospital, at 4D Médica we are specialists in the sale of radiological medical equipment and we offer an optimal after-sales service. Ask us about our equipment without obligation.
Contact 4D Médica
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.