An ultrasound, also called a sonogram or ultrasound, is an ultrasound scan. diagnostic imaging test that uses the sound waves to create images of organs, tissues and internal structures of the organism. It is a simple, safe and non-invasive technique which allows health professionals to analyze and observe the inside of the body without surgery. In other words, it is a diagnostic technique that no need to make any incisions or use ionizing radiationas in the case of the X-rays.
It stands out for being a comfortable, economical and painless test. It is mainly used for diagnose various medical conditionshealth monitoring and development of the baby during pregnancy and guide certain medical proceduressuch as biopsies, tissue extraction, and other techniques that require the use of image diagnosis.
How does an ultrasound scan work?
An ultrasound is a technique that emits a series of mechanical waves that have a frequency above the hearing ability of the human ear and allow create two-dimensional and three-dimensional images. These images are called sonograms and are performed with specific equipment. The medical devices that allow these diagnoses to be performed are ultrasound scanners. They have a tool rod-shaped which is known as transducer and is responsible for detecting the waves produced in the different tissues, organs and fluids of the body. These are then picked up again by the transducer and converted into electrical signals.
In order to analyze the waves, a special gel on the skin in the area to be examined. Through the use of a computer, these signals are processed to create a real-time image of internal structures of the organism. The images produced are visualized on the screen and provide information on movements that are occurring, the distance at which a fabric is locatedas well as its size, shape and composition.
Types of ultrasound scans: Uses and main differences
We can find different types of ultrasound: ultrasound in pregnancy, diagnostic medical ultrasound, guided ultrasound, as well as 3D and 4D ultrasound. Let's see their main differences:
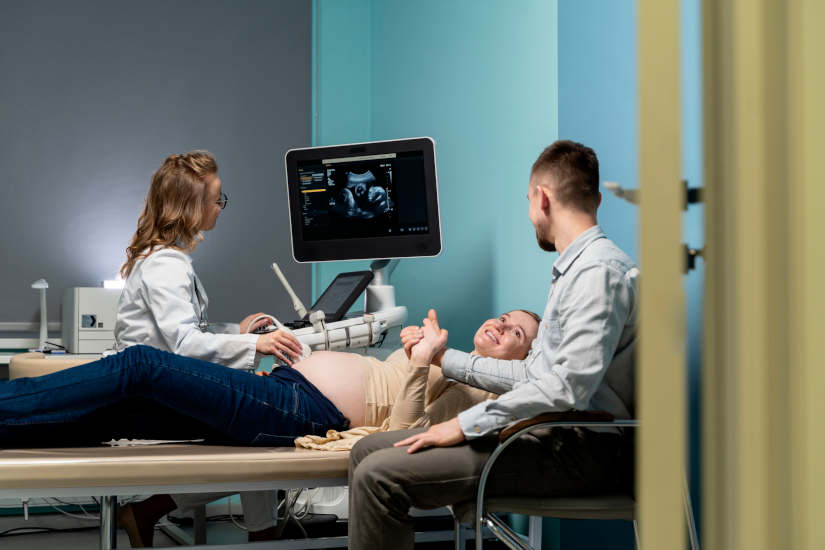
Ultrasound in pregnancy
Ultrasound in pregnancy, also known as obstetrical ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging test that provides the visualization of the fetus inside the mother's uterus. As it is an ultrasound technique that does not involve radiation, it is a safe technique for mother and baby.
What is fetal ultrasound used for?
It allows analysis of the baby's growth, health and general development. In particular, it provides the following information:
- Confirmation of pregnancy.
- Verification of multiple pregnancy (twins and triplets).
- Knowledge of the gestational age. That is, how far along the pregnancy is.
- Analysis of the sizethe position of the fetus, the growth and the sex of the baby.
- Diagnosis of congenital defects in the various parts of the baby's body, such as the brain, heart or spinal cord.
- Study of the existing amount of amniotic fluid. It is essential for the development of the baby's lungs and bones, as well as to protect the baby from injury.
- Identify problems in the placenta, uterus, cervix and ovaries of the mother.
- Information on possible signs that could indicate an increase in the number of risk of Down syndrome.
Diagnostic medical ultrasound
Diagnostic medical ultrasound is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of study of diseases or possible health problems in the patient. This type of test is used when a person detects certain symptoms that are important to analyze. Using this type of ultrasound, medical professionals can study various medical conditions involving different parts of the body. Depending on the area to be analyzedwe can distinguish different modalities of diagnostic medical ultrasound scans:
- Abdominal ultrasoundIt focuses on the observation of the internal structure of the abdomen. It allows to analyze organs such as the pancreas, kidneys, liver, gallbladder and spleen.
- Vaginal ultrasoundVaginal ultrasound: This test is used to analyze the uterus, ovaries, endometrium, cervix, fallopian tubes and pelvic area of the woman. Vaginal or tansvaginal ultrasound is used to detect possible gynecological conditions, such as the presence of ovarian cysts, fibroids and uterine fibroids, abnormalities in the menstrual cycle, certain types of infertility and pelvic pain.
- Rectal ultrasoundRectal examination: Consists in the evaluation of the rectum to study the prostate and bladder function.
- Renal ultrasoundKidney ultrasound: Evaluates the condition of the kidneys, both the size, location and shape, as well as their adjacent structures. This type of ultrasound helps detect the presence of tumors, cysts and renal obstructions.
- Breast ultrasoundIt is used to detect abnormalities in the breast tissue, such as the presence of cysts. It is often used as a backup technique after mammography.
- Cervical and thyroid ultrasoundAnalyzes the functioning of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. It is essential to study possible health problems that may arise, such as the appearance of nodules, cysts and structural alterations. It is also used to analyze the salivary glands.
- Doppler or vascular ultrasoundThe speed and direction of blood flow in the heart and blood vessels can be analyzed with this ultrasound. It allows to measure the blood circulation in the different organs of the body, as well as the neck, arms and legs. It is an essential test to diagnose possible blockages, narrowing and problems in the circulatory system.
- Muscle ultrasoundMusculoskeletal ultrasound: This ultrasound is also called musculoskeletal ultrasound. It explores the different muscles, tendons, ligaments, bursae, cartilage, joints and bone surfaces, making it possible to detect the presence of injuries, tendinitis, degenerative problems and other conditions of the muscular tissues.
Guided ultrasound
Guided ultrasound is a technique used for the diagnosis and treatment of development of ultrasound-guided procedures. It is used to guide health care professionals in the Performing tissue biopsies, tissue aspiration and removal, catheter placement, abscess drainage and percutaneous injections.. This technique consists of the introduction of a needle or catheter into the area of the body to be tested. Transducer advancement is controlled in real time, allowing the needle to be steered for more accurate medical diagnosis.
This type of ultrasound can be performed in two ways: through devices adapted to the probes or through the hands-free techniquewhere the professional holds the needle with one hand and the probe with the other hand.
3D and 4D ultrasound
The technological advances in the field of medicine allow the images generated in an ultrasound scan to be displayed in 3D and 4D. The 3D ultrasound scans emerged at the end of the 1990s and offer a wide range of high-resolution static images with a three-dimensional perspective. Currently, the systems used are based on mechanical transducerswhich make it possible to obtain images in the three perpendicular planes. Thus, in the image, the following can be seen transverse, longitudinal and coronal sections. As for the 4D ultrasound scansincorporate a technology that captures motion in real timeThis provides a closer and more realistic reproduction of what is happening inside the organism.
In which cases are 3D and 4D ultrasound scans used?
The 3D ultrasound scans are used in pregnancy and in various specialties. such as gastroenterology, gynecology and obstetrics, breast and uterine pathology and cardiology. It also plays an essential role in vascular surgery, urology, rheumatology and traumatology.
For their part, the 4D ultrasound scans are used during pregnancy to analyze the baby's development. By providing real-time motion, shows the gestures and movements made by the baby inside the uterus and also serves to detect possible problems and anomalies. It is recommended to be performed around the 28th week of gestation.This is the moment when the fetus is more developed and its features are more similar to those of a newborn. At the same time, in 4D ultrasounds, it is essential that there is a sufficient amount of amniotic fluid. This is a fundamental aspect for the ultrasound waves to be transmitted properly. Otherwise, the image will be displayed with lower quality, so it would not be advisable to use this technique.
However, it should be noted that 3D and 4D ultrasound scans are not a substitute for follow-up ultrasound scans. which must be performed at 12, 20 and 32 weeks of gestation. Therefore, it is a complementary test for more information on fetal growth.
Innovations in the field of ultrasound
In the field of diagnostic imaging, the ultrasound scanners are the devices used to perform ultrasound scans. In recent years, numerous advances have led to the development of a new type of ultrasound system. medical equipment adapted to new needs of medical centers, hospitals and health professionals.
In addition to the traditional ultrasound scanners that allow a simple and safe test to be performed, the following have emerged new generation ultrasound scanners that use the latest technology and are equipped with artificial intelligence. This type of ultrasound scanners are portable and are characterized by the fact that they can be used completely remotely. In this way, professionals do not have to be present in medical centers and can reach many more regions and patients. Undoubtedly, a a key aspect to boost telemedicine and create fast, complete and accurate diagnostics.
In conclusion, ultrasound scans are one of the most important The most widely used medical diagnostic imaging techniques in use today. This is because it is an easy, safe and non-invasive test that is very useful for diagnosing certain medical conditions, for analyzing the development of the baby during pregnancy and also as a support technique for other procedures. In most cases, ultrasound is part of the first diagnosis to then evaluate how to proceed and what other tests should be performed when treating an ailment or disease.
Bibliography
Your Health Channel. (n. d.). 4D ultrasound: What you need to know. https://www.tucanaldesalud.es/es/voz-especialista/ecografia-4d
MedlinePlus (n. d.). Ultrasonography. https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/pruebas-de-laboratorio/ecografia/
MyDiagnosis (n. d.). Ultrasound: procedure, uses and advantages. https://midiagnostico.es/ecografia-procedimiento-usos-y-ventajas/
Del Cura, J. L., Zabala, R., & Corta, I. (2009). Intervencionismo guiado por ecografía: lo que todo radiólogo debe conocer / US-guided interventional procedures: what a radiologist needs to know. Radiology, 52(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rx.2010.01.014