por Kiko Ramos | Dec 27, 2024 | Equipment analysis
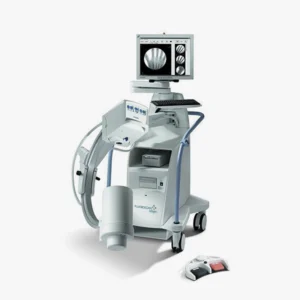
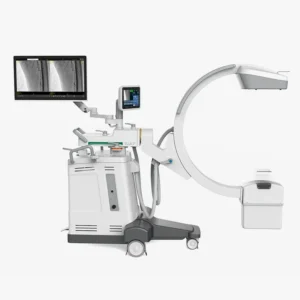
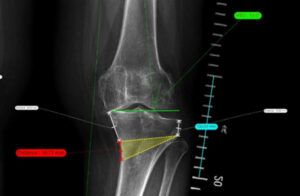
The arc in C is specialized medical equipment used in radiology and interventional procedures to obtain real-time X-ray images of the inside of the human body. It is a mobile device that enables radiological and fluoroscopic imaging. Its name derives from its C-shaped structure"which allows a wide range of movements and the acquisition of images from multiple angles and positions for capture specific anatomical views without moving the patient.
It is used to obtain X-ray and fluoroscopic images without having to move the patient to the radiology department. Therefore, diagnostics and procedures can be performed at the patient's hospital bedside or on the operating table during surgery. Its use is essential in areas such as surgery, orthopedics, traumatology, cardiology, neurology, urology and minimally invasive procedures.
Among the main advantages offered by the arc in Cis that facilitates diagnosisoffers a high precision and safety, y decreases the duration of surgical interventions in which the patient is under general anesthesia. In the following article, we analyze how a C-arm works, its parts, functions and main applications and uses. medical equipment.
How does a C-arc work?
The operation of a surgical C-arm is similar to that of the X-ray machines conventional. Combine two main elements that work in an integrated manner How does this process work?
X-ray generator
The process begins with the X-ray tubelocated at one end of the "C" arm. This component emits a beam of radiation which passes through the patient's body. Collimators, which are adjustable devices on the tube, delimit the radiation field, ensuring that only the area of interest is irradiated. This not only improves image quality, but also minimizes radiation exposure to other areas.
When the X-ray beam passes through the patient's body, interacts with the different tissuesgenerating a phenomenon called differential absorption. The Denser tissues, such as bones, absorb more radiation. and are represented as white areas in the image. On the other hand, the soft tissues and air-filled areas allow the rays to pass through more easily, appearing in gray or black tones. This difference in absorption is what creates the contrast in radiological images.
Image detector or intensifier
At the opposite end of the X-ray tube is the image detector or intensifier. This component receives the rays that have passed through the patient and converts them into electrical signals. Modern detectors, called digital flat panel detectors, process these signals to generate high-resolution images. This advance has largely replaced traditional intensifiers, offering greater sharpness and less radiation exposure.
The signals captured by the detector are sent to a processing system that converts the data into digital images.. This software automatically optimizes parameters such as contrast, brightness and sharpness to ensure that images are clear and easy to interpret. These images are displayed in real time on monitors connected to the system, allowing the medical team to observe the area of interest while the procedure is being performed.
Meet our 4D Medical equipment
C-arc: Parts and functions
The C-arm in radiology consists of several parts that work together to provide high quality images in real time during medical procedures. Below are its main components and functions:
| Part |
Description |
| C-shaped arm |
Central structure connecting the X-ray tube to the detector. |
| X-ray tube |
Located at one end of the C-arm, it emits the radiation beam. |
| Image detector |
At the opposite end of the X-ray tube, it captures the radiation passing through the patient. |
| Mobile base |
Wheeled structure that supports the equipment and facilitates its transport. |
| Control panel |
Operational console from where the equipment parameters are adjusted. |
| Monitors |
Screens connected to the image processing system. |
| Collimator system |
Adjustable device located in the X-ray tube. |
| Cooling system |
Components that dissipate the heat generated by the X-ray tube. |
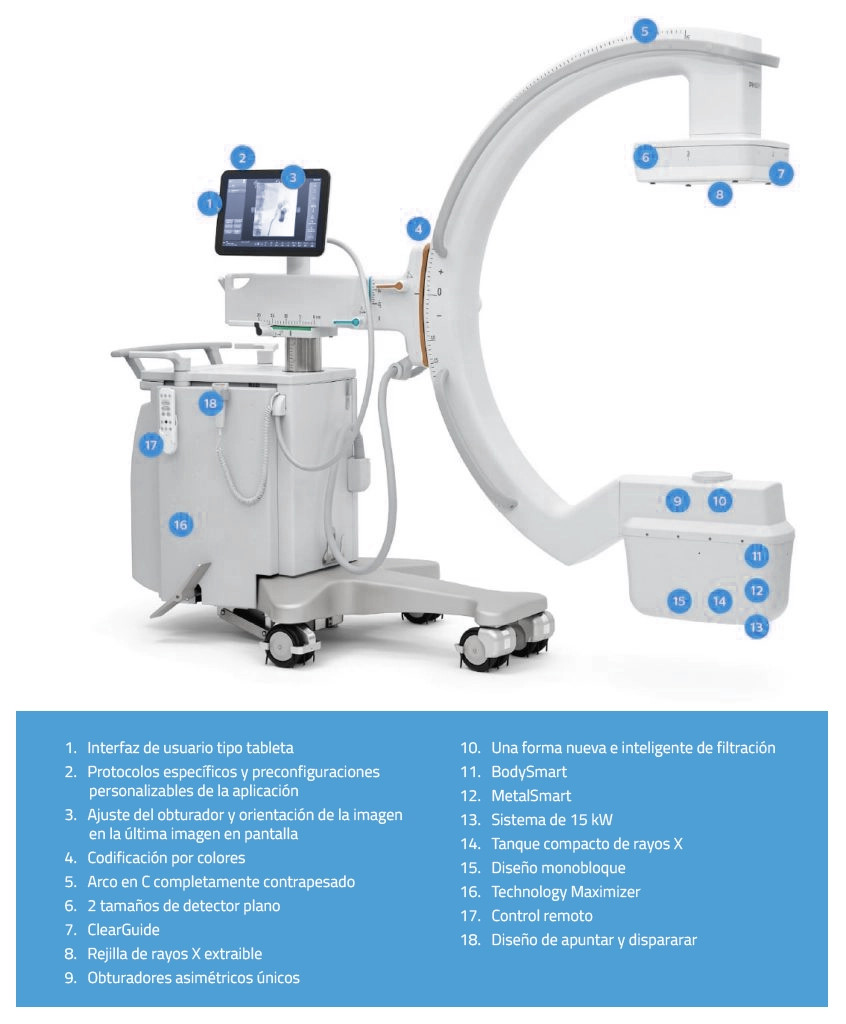
Parts of a C-arc
1. "C" shape arm
It is the main structure that connects the essential components of the equipment, such as the X-ray tube and the imaging detector.
Functions:
- The C-shaped arm connects the X-ray tube, which is located at one end, to the image detector or intensifier, which is located at the opposite end, allowing a wide range of movement around the patient.
- Facilitates imaging from multiple angles no need to move the patient.
- Includes rotations in multiple planes: horizontal, orbital and verticalThis makes it possible to adapt to different types of procedures.
X-ray tube
This is the radiation generator located at one end of the C-arm.
Functions:
- Emits X-rays through the patient's body.
- Its intensity and duration are controlled to obtain quality images. while minimizing radiation exposure.
- Security is a key aspect in the use of the C-arm. These devices are designed to minimize radiation exposure for both the patient and the medical staff. They have specific systems that reduce scattered radiation and integrated dosimeters continuously monitor the delivered dose.
3. Image intensifier or digital flat detector
It is located on the opposite side of the X-ray tube, capturing the radiation passing through the patient.
Functions:
- Converts X-rays into visible images in real time.
- The state-of-the-art digital flat panel detectors offer higher resolution images and lower radiation exposure compared to traditional intensifiers.
4. Control Console
This is the external control panel operated by the radiological technician during diagnosis.
Functions:
- Allows adjustment of exposure parametersThe company has a wide range of products, such as time and intensity, among other aspects.
- Controls the movement of the arc and the orientation of the images.
- Saves and transmits the images obtained for further analysis. The data is stored in a PACS system (Picture Archiving and Communication System), allowing quick and easy access for further analysis.
3. Monitor
The C-arm includes one or more high-resolution monitors, usually in Full HD, which allow physicians to view images in real time during procedures. This screen is connected to the system, usually located near the surgical field.
Functions:
- Displays radiological and fluoroscopic images in real time so that physicians can be guided through the procedure.
- Some systems include dual monitors to compare images in real time with previous analyses.
6. Mobility system
It is a rolling base with lockable wheels or fixed support system on larger models.
Functions:
- Facilitates C-arm transport between different areas of the hospital.
- Allows you to position the equipment in a stable and safe manner around the patient.
7. Power generator
It provides the power needed to operate the X-ray tube and other system components.
Functions:
- Regulates the power supply to ensure consistent performance during use.
8. Image processing software
By means of a radiodiagnostic softwareThe computerized system manages the acquisition, processing and storage of medical images.
Functions:
- Improved image quality through techniques such as contrast adjustment and noise reduction.
- Allows measurements and annotations directly on the images.
9. Collimator system
It is the device located in the X-ray tube that is responsible for controlling the irradiated area to be analyzed or treated.
Functions:
- Adjusts the radiation field to focus only on the area of interest.
- Reduces unnecessary radiation exposure for both the patient and the medical staff.
10. Refrigeration system
The cooling system is the mechanism for dissipating the heat generated by the X-ray tube.
Functions:
- Maintains equipment temperature within safe operating limits.
- Prolongs X-ray tube lifetime.
Clinical uses and applications of a C-arm in radiology
The C-arm is a medical device widely used in radiology and in the speciality of interventional radiology What are its main uses and clinical applications?
Orthopedic surgery
In the field of orthopedic surgery, the C-arm is essential for the precise placement of screws, intramedullary nails and plates used in orthopedic surgery. fracture treatment. It is also used for guiding fracture reduction or deformity correction procedures. Its ability to provide clear, real-time images allows the surgeon to visualize bone structures and ensure that implants are positioned correctly, reducing the risk of errors during surgery.
Spine surgery
In spinal interventions, the C-arm facilitates the precise placement of the fixation devices such as pedicle screws and spinal fusion brackets. In turn, it is also used in procedures such as the vertebroplasty. The real-time images it generates are crucial to avoid injury to sensitive nerve structures and to ensure a successful outcome.
Interventional radiology
The C-arm is an essential tool in interventional radiology, where it is used for guided procedures such as biopsies, drains and tumor ablations. It is also indispensable in angiographieswhere digital subtraction imaging (DSA) allows high-precision visualization of blood vessels. This equipment facilitates minimally invasive procedures, which require detailed, real-time imaging to ensure accurate results.
Interventional cardiology
In cardiology, the C-arc is used in procedures such as coronary angiographieswhich evaluates the circulation in the arteries of the heart. It is also key to the implantation of pacemakers and other cardiac devices. Thanks to the dynamic images it provides, physicians can perform complex procedures with greater safety and precision.
Vascular surgery
In vascular surgery, the C-arm allows detailed visualization of the vascular system, which facilitates procedures such as the stenting to repair aneurysms or the insertion of filters in the vena cava.
Urology
In urology, this equipment is used to guide procedures such as placement of ureteral catheters or nephrostomies. It is also useful in the percutaneous nephrolithotomywhere kidney stones are removed using minimally invasive techniques. Real-time imaging helps physicians locate specific structures and avoid damage to surrounding tissues.
Gastroenterology
In gastroenterologic procedures, the C-arm is used for inserting feeding tubes or drainsas well as for placing esophageal prostheses. This device is especially useful in delicate procedures where precision is crucial, such as in hard-to-reach areas within the gastrointestinal tract.
Neurosurgery
In neurosurgery, the C-arm is used for procedures such as the electrode placement for deep brain stimulation or minimally invasive spinal surgeries. The ability to generate highly accurate intraoperative images is critical for navigating complex structures of the nervous system and ensuring patient safety.
Oncology
In the treatment of cancer, the C-arm is a valuable tool for radiofrequency or microwave ablationswhere localized tumors are destroyed. It is also used for the placement of markers to guide radiation therapy. Its ability to generate precise images allows for accurate positioning of instruments in malignant tissues, optimizing treatment.
Traumatology
In emergency situations or in traumatology, the C-arc is used for evaluate complex fractures and guide reduction procedures. It allows to verify in real time the correct alignment of the bones, which is crucial to ensure the patient's functional recovery.
Emergency procedures
In emergency environments, this equipment is indispensable for the immediate evaluation of serious injuriesas major trauma, and for guiding critical procedures such as thoracic drainage. Its ability to generate immediate images allows physicians to make quick decisions and save lives in critical situations.
Dentistry and maxillofacial surgery
In dentistry and maxillofacial surgery, the C-arm is used for the dental implant placement and surgical planning in the mandibular region. Provides detailed images of the bony structures of the skull and jaw, ensuring accurate results.
Gynecology and obstetrics
In gynecology, this equipment is used for interventional procedures, such as the placement of intrauterine devices or catheters used in fertility treatments. Its use improves the accuracy of procedures in sensitive areas, increasing safety and effectiveness.
Conclusion
The C-arm stands out for its versatilityas it is used in multiple medical specialties. Its ability to provide real-time imaging facilitates decision-making during complex procedures, reducing errors and improving clinical outcomes. In addition, by enabling minimally invasive interventions, it contributes to faster patient recovery and greater efficiency in medical resources.
If you are a health professional and you are interested in to acquire a C-arc or any other radiodiagnostic equipment, our 4D team will contact you to advise you and find the best solution for your clinic or hospital.
Contact 4D
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Médica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.

por Luis Daniel Fernádez | Dec 18, 2024 | Equipment analysis
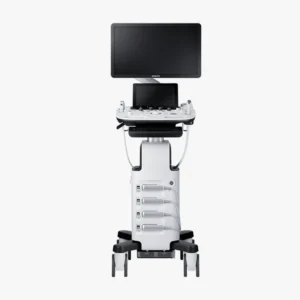
Ultrasoundultrasonography, also known as ultrasonography, is a non-invasive technique using ultrasound to obtain real-time images of the inside of the body. For this purpose, a medical equipment specific: the ultrasound scannerHow does it work and what types of ultrasound scanners are available on the market? We address this in the following article.
The ultrasound scanner: How does it work?
The ultrasound scanner is a medical equipment in the field of image diagnosis. It employs a device called a transducer which emits high-frequency sound waves, called ultrasound. These waves are inaudible to the human ear and travel through the different internal tissues of the body. At the moment when the waves encounter the various organs and structures, it is when are reflected as echoes. These echoes are picked up by the transducer and generate the medical images that can be displayed on a screen. These images are known as ultrasound scans and allow professionals to evaluate different tissues and internal organs of the organism.
In the realization of a ultrasoundis used, a transducer that glides over the skin in the area to be analyzed. This device is coated with a conductive gel that facilitates the transmission of ultrasound waves. It has the function of eliminating the air that exists between the skin and the transducer, helping to improve the quality of the images. In an ultrasound scan, the following can be obtained still images and also allows to observe the movement in real time. It is an essential medical equipment in medicine that has the function of analyzing the state of organs such as the heart or blood flow.
Meet our 4D Medical equipment
Parts of an ultrasound scanner
An ultrasound scanner consists of the following components:
| Parts of an ultrasound scanner |
Description |
| Transducer or probe |
Device in charge of emitting and receiving ultrasonic waves. |
| Monitor |
Screen where the images generated by the ultrasound scanner are displayed. |
| Control panel |
Interface with buttons and controls to adjust parameters and settings. |
| Central processing unit |
Processor that handles the data and generates the ultrasonic images. |
| Storage system |
Allows to save images and data obtained during diagnosis. |
| Power supply |
Provides electrical power to the device. |
| Software |
Program that controls the operation of the ultrasound scanner and processes the images. |
| Handles and wheels |
Facilitate the mobility of the equipment within the hospital or clinic. |
| Ports and connections |
They allow the connection of accessories and additional devices. |
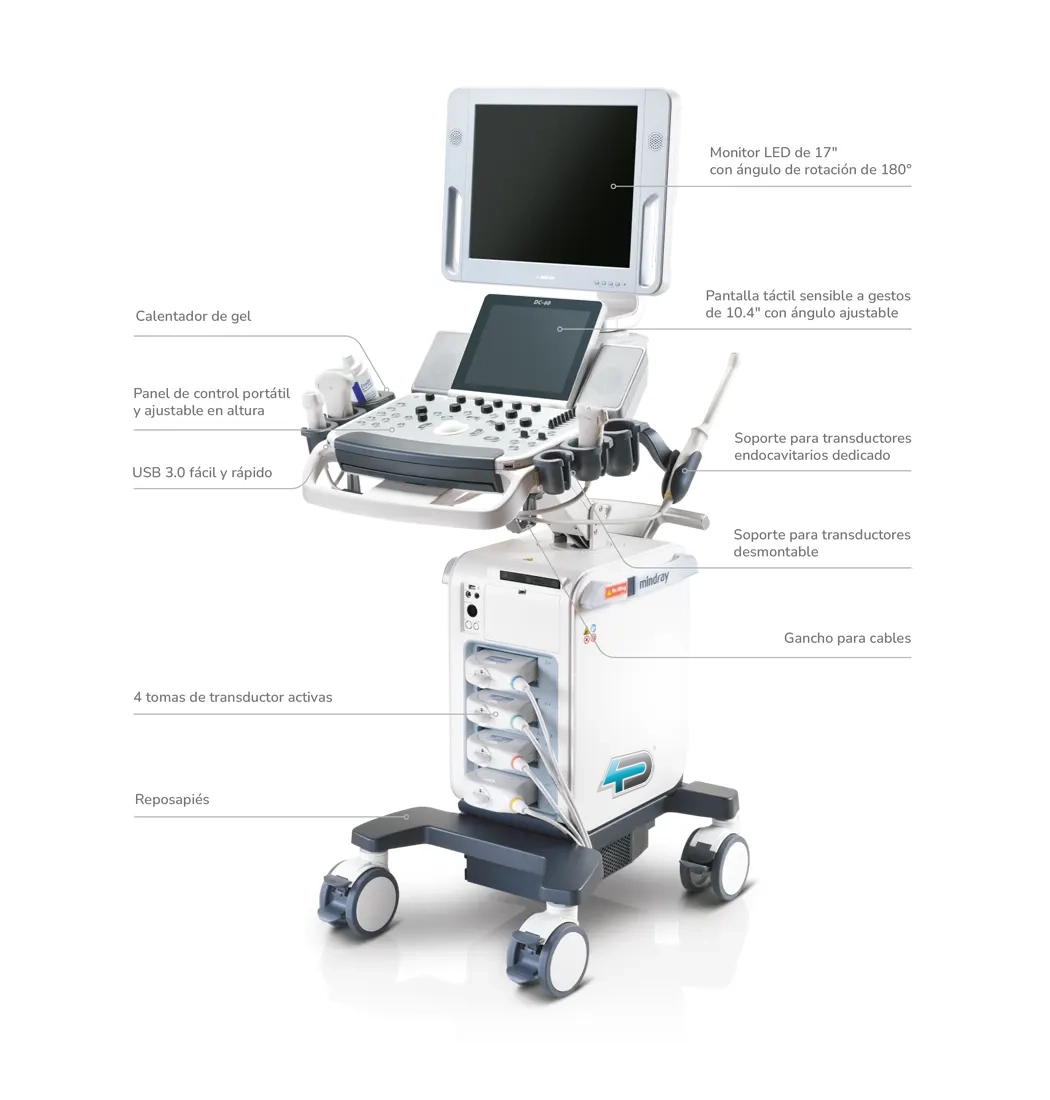
Detailed image of the parts of an ultrasound scanner
Transducer or probe
It is the main part of the device, responsible for transforming electrical signals into ultrasound waves. They are made of piezoelectric material and function as ultrasound emitters and receivers. There are different types of transducers:
Depending on its use
- LinearThey are used for superficial and vascular studies. They generate rectangular images and use high frequencies, since they do not require much penetration, being useful in the exploration of ligaments, tendons, muscles, thyroid, scrotum, breast and superficial vessels.
- Curved or convexThey have a curved shape and produce trapezoidal images. They are used with low frequencies because they are designed to explore deep structures, as in obstetrics and abdominal studies in general.
- Endocavitary or intracavitaryThey can be linear or convex. Their frequency varies according to the required penetration. They are used in intravaginal and intrarectal studies, for gynecological or prostate examinations.
- SectorialThey are a variant of the convex transducers and offer triangular or fan-shaped images. They use frequencies similar to those of curved transducers and allow an intercostal approach, so they are used in cardiac and abdominal studies.
According to frequency
- High frequency (up to 15 MHz)They are used to explore small and superficial structures.
- Low frequency (approximately 2.5 MHz)They are used for ultrasound scans that require a greater depth of penetration.
Monitor
Displays the images generated by the processing unit.The image is displayed on the monitor, so that professionals can observe and evaluate the state of the different anatomical structures in real time. Most current monitors can reproduce images in grayscale and color.
Control panel
It is located in the front part of the ultrasound scanner and allows the ultrasound specialist to make various adjustments to the equipment configuration. It allows to modify the brightness, the sharpness of the images and the frequency of the sound waves. In addition, it also allows to configure the necessary parameters to carry out the type of ultrasound that the patient requires.
Central processing unit
It is the component that receives the information provided by the probe. It converts the signals into electrical impulses and generates the image of the anatomical part of the area to be analyzed.
Storage system
It is the internal element that allows to save images and patient's data for further analysis. It can consist of an internal memory, USB or be connected to a PACS system (Picture Archiving and Communication System).
Power supply
Provides power to the ultrasound machineThe power supply is provided either by alternating current or by rechargeable batteries in the portable models.
Software
It is essential for processing ultrasound signals and generating medical images. It can include specific modules for different types of studies, such as cardiology or gynecology, among other areas.
Handles and wheels
These elements facilitate handling and transport of the equipmentespecially in the case of mobile ultrasound scanners.
Ports and connections
This type of components included in the ultrasound scanners are used for connect multiple probes, USB devices or DICOM interfaces to share images.
Types of ultrasound scanners
Having analyzed the operation of an ultrasound scanner and its main components, we can differentiate between different types of ultrasound scanners:

Imaging technology
1. 2D ultrasound scanners
- These are the most common and basic models. Generan two-dimensional images in real timeThey are widely used in the obstetrics area, to perform general and abdominal studies.
- Main applicationsBasic analysis, pregnancy control and organ evaluation.
2. 3D ultrasound scanners
- Allow display three-dimensional structures in real timeproviding greater detail. They are useful for creating more accurate images of fetuses and studying structural abnormalities.
- Main applicationsThey are used in advanced obstetrics and for surface studies of organs and tumors.
3. 4D ultrasound scanners
- They add the time dimension to 3D imagesallowing to see the movement in real time. It is especially useful in the obstetrics area to see fetal movements.
- Main applicationsObstetrical diagnosis and dynamic studies of joints.
4. Doppler ultrasound scanners
- They use the Doppler effect for assessing blood flow in vessels and organs. There are different models and variants:
- Color DopplerThey offer a color representation of the blood flow.
- Pulsed Doppler technologyThey provide a more detailed analysis of blood flow velocities.
- Continuous DopplerThey measure very fast flows.
- Main applicationsThey are used for vascular, cardiac and circulatory studies.
5. Tissue Doppler Ultrasound Scanners
- They are in charge of making a specific evaluation of the movements of the heart tissues and blood flow.
Mobility
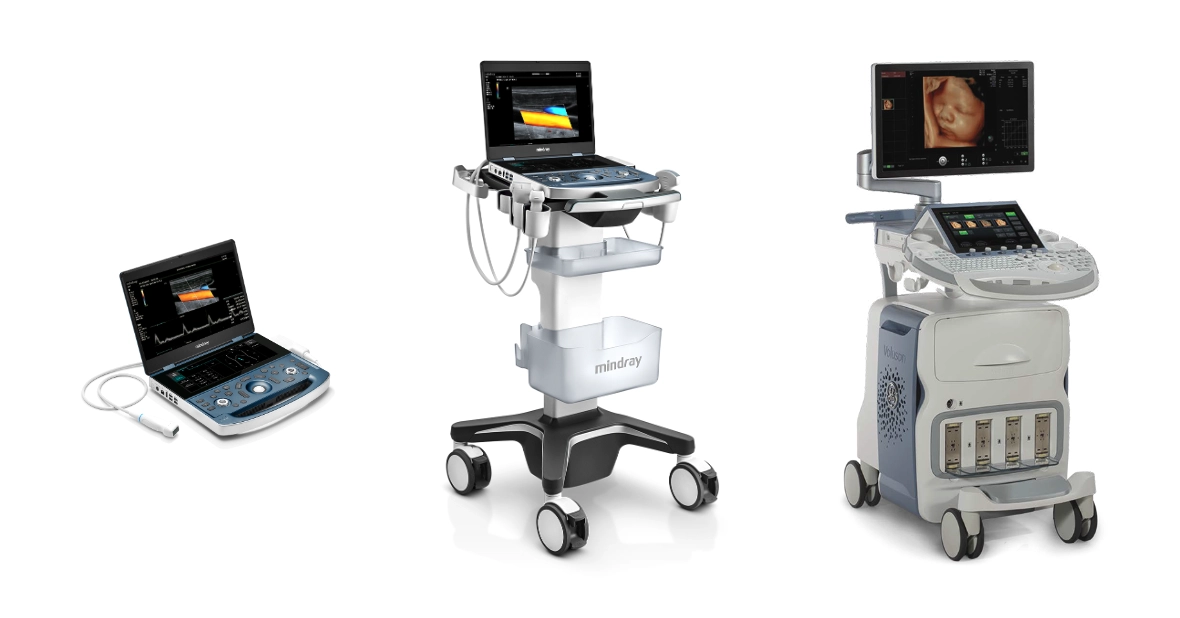
1. Portable ultrasound scanners
- They are small and lightweight devicesThey are ideal for home transport, emergency or remote areas. There are multiple versions that include advanced technologies, such as 2D ultrasound, Doppler, etc.
- Main applicationsThey are used for emergencies and ICU, mobile clinics and medical visits to remote areas.
2. Trolley or console ultrasound scanners
- They are larger and more robust models. They have a fixed console that offers a variety of functions and high-resolution imaging options.
- Main applicationsThey are used in hospitals and specialized clinics.
3. Wireless ultrasound scanners
- They are connected to mobile devicesThe medical imaging systems, such as tablets or smartphones, through applications. They are characterized by high portability and immediate access to the generated medical images.
- Main applicationsThey are used in sports medicine, emergencies and telemedicine.
Clinical Specialty
1. Obstetrics and gynecology
- This type of transvaginal ultrasound scanners are specialized in the visualization of the fetus, uterus and ovaries of women.
2. Cardiac (Echocardiograms)
- They are designed to evaluate the structure and heart function, valves and blood flow.
Vascular
- They are used for analize arteries and veinsmeasuring the flow and detecting obstructions or thrombi.
4. Musculoskeletal and Physical Therapy
- Allow visualizing muscles, ligaments, tendons and joints. These physiotherapy ultrasound scanners are used in sports medicine to detect injuries or to analyze the recovery from an injury.
5. Abdominals
- They are oriented to the study of abdominal organs like the liver, kidneys, spleen or pancreas.
6. Neurological
- They are used for assessing the brainespecially in neonates.
7. Urological
- These devices are designed to examine the kidneys, bladder and prostate of the male.
8. Endoscopic
- They combine ultrasound with endoscopes to obtain internal images of the digestive tract or areas of difficult access.
Resolution and advanced technology
1. High resolution
- This type of medical equipment offers images of the highest qualityIt is therefore especially useful in complex applications.
2. Ultrasound scanners with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Type of purchase
1. New ultrasound scanners
New ultrasound scanners are newly manufactured, previously unused ultrasound machines with the latest technology upgrades and full manufacturer's warranties. They feature the following characteristics:
- State-of-the-art technologyThey incorporate the latest innovations in imaging, such as advanced Doppler, elastography, 3D and 4D ultrasound and even artificial intelligence.
- Full warrantyThey offer extensive warranties that are backed by the manufacturer, generally from 1 to 5 years.
- CustomizationYou have the possibility to configure the equipment according to your specific needs, including transducers and software.
- Longer service lifeSince they have no previous use, their potential useful life is longer, especially if proper maintenance is carried out.
- Certifications and technical supportThey comply with all current quality and medical safety standards. In addition, they have specialized technical support.
2. Second-hand or opportunity ultrasound scanners
The used ultrasound scanners are previously used ultrasound devices that have been reconditioned or overhauled to ensure their functionality before being sold again. These devices may come from clinics, hospitals or doctors' offices that have refurbished them for newer models or no longer need them. Compared to new models, they have the following features characteristics:
- Technical reviewBefore being sold, ultrasound scanners undergo a series of quality tests to ensure that they are functioning properly. These may include repairs, cleaning, calibration and software upgrades.
- Reduced priceThey are less expensive than new equipment, which makes them attractive for small clinics, independent physicians or institutions with limited budgets.
- Variety of modelsYou can find from basic ultrasound scanners to advanced equipment with technologies such as Doppler or 3D.
- Limited WarrantySome suppliers offer warranties, but these are usually shorter than those for new equipment.
- Variable statusThe performance and service life of used ultrasound scanners will depend on how well the device has been maintained during previous use.
Conclusion
The ultrasound scanner is a medical equipment that is widely used in the field of diagnostic imaging to perform one of the most popular medical tests: ultrasound. Depending on the technology, mobility, medical specialty and type of purchase, different types of ultrasound scanners can be found.
There is a wide range of ultrasound scanners on the market that adapt to each of the medical needs. If you need more information, contact us and from 4D Médica we will offer you personalized advice so that you can choose the most suitable ultrasound scanner for your center.
Contact 4D
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.


por Luis Daniel Fernádez | Dec 13, 2024 | Equipment analysis
The technology has had a significant impact on the healthcare system, especially in the radiology area. In recent years, one of the most relevant changes following the advent of the Internet has been the use of computerized systems in the field of image diagnosis. This has allowed the development of a digital imaging department where medical information can be managed and stored conveniently and securely.
In a digital imaging department, we can distinguish three fundamental tools: the PACS system, the RIS system and the HIS system. In the following article, we analyze what the PACS system is, how it works and its relationship with the RIS and HIS system.
What is the PACS system in radiology?
The term PACS stands for Picture Archiving and Communication System, which refers to Image Archiving and Communication System. This is a computer software used in the radiology area for the following purposes store, manage, present and share medical images and diagnostic procedure reports electronically.
Before the advent of the PACS system in radiology, the images generated after diagnostic examinations were stored in a physical format, mainly as radiographic films. Therefore, from the time the medical test was performed, there was a long process until the final image was obtained. With digitization, it is now possible to resort to a AI software for the different medical teams to obtain an accurate faster and more efficient access to informationwhich will allow optimize workflow in clinical practice.
How does the PACS system work?
A PACS system consists of a series of mechanical and electronic components which are connected to each other by a copper or fiber optic communication network. Specifically, we can differentiate between four main components:
- Image acquisition hardware
- Workstations for image interpretation and review
- Servers for storage and transmission of images
- Network for data transmission
All these elements work in an integrated manner to allow medical images to be captured, stored, distributed and displayed digitally. Through the use of this network, the graphic information generated in different studies, such as a CT scan, is transmitted to the magnetic resonance imaging o TAC.
How does this process unfold?
First of all, data from the system servers is passed to the archiving drives. Subsequently, they are distributed to the stations where radiological physicians review the generated medical images and also to the teleradiology serverswhich allow access to the archive through the Internet.
With a digital radiology PACS system, you can view images remotely from any medical department, office or externally. To do so, health care personnel have special identification codes which allows them to access diagnostic tests for each patient.
The DICOM medical imaging communication standard
For information and images to flow through the PACS system components, it is necessary to comply with the DICOM medical image communication standard. DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine and is a standard for the communication of medical images. standard for digital storage and transmission of medical images and related patient information.
It is responsible for define the file format and structure and, in turn, includes a communications protocol to facilitate connectivity between medical devices and systems. However, it should be noted that the majority of modern devices and medical equipment current DICOM images are produced.
Advantages of using a PACS system in radiology
We analyze the main advantages offered by a PACS system in the management of radiological images:
Improved workflow in radiology departments
Radiologists and medical teams involved in the diagnostic imaging process can access and review digital images from any workstation on the hospital's network or remotely through the web server. This allows rapid consultation of studies and collaboration between physicians and specialists.
Error reduction
As the format of medical images is no longer physical, eliminating the possibility of duplicate diagnoses and also reduces both the risk of loss as the damage of the generated medical images.
Integration with other IT systems
One of the main advantages of the PACS system is that it allows the integration with other IT systems that can be used in health careThe RIS (Radiological Information System) and HIS (Hospital Management Software).
Capacity to store large volumes of data
Not only is it essential for clinical management and patient care, being able to store large volumes of medical imaging data is a key aspect for research and education in the area of health and medicine. In this way, researchers can access image databases for studies and students in training can use many of the images as educational material.
More accurate and detailed diagnosis
The use of the PACS system provides a more detailed reading of the diagnoses. This is mainly because the images are reviewed on high-resolution monitors and can be manipulated more accurately, which helps to detect abnormalities present in the image more quickly and accurately.
Saving time and resources
Another of its advantages is that it offers a time saving and a decrease in the workload of the staff.The cost of printing X-rays and other radiological elements was also reduced. At the same time, waiting times and resources at the hospital level are reduced.
Relationship between the PACS, RIS and HIS system
PACS, RIS and HIS are three systems key components in the digital health informatics ecosystem. Their interrelation is essential for the efficient functioning of the healthcare services of any clinic, health center or hospital. While the PACS system in radiology is used to manage, store and share images of the different diagnostic imaging procedures, the RIS and HIS system have other functions. What is each used for and what is the relationship between them?
The RIS system
The RIS system or Radiology Information System, is the program that runs the digital radiology department. It is a software that contains all the information of the radiology area and hospitals, thus enabling manage information and processes related to diagnostic imaging services.
Functions performed
- Scheduling of appointments and studies
- Order generation
- Recording of results with the generated medical images
- Workflow management in the radiology department
The HIS system
As for the Hospital Information System (HIS), it is a system of hospital information system. By using it, all the data are stored in the data related to the management and administration of a hospital. It is designed to manage all areas involved in the operation of a hospital from a single platform.
Functions performed
- Management and scheduling of medical appointments
- Patient care: Administration of patients' medical records and results of medical examinations performed.
- Human Resources
- Billing
- Monitoring the quality of medical care
Interaction of PACS, RIS and HIS systems
- HISThe central system that coordinates and stores all patient information in a clinic or hospital facility, including demographic, clinical and financial data.
- RISIt communicates with the HIS system to obtain relevant patient information and to manage the radiology area. It is used to schedule radiological procedures requested from other areas of the hospital.
- PACSRIS-PAC: Works hand in hand with RIS to store and manage the medical images generated by the requested studies. The RIS-PAC interaction allows the report to be presented in both systems so that each report appears linked to the images of the study performed.
Conclusion
The PACS system is a fundamental tool in the radiology area to be able to store and manage medical images digitally. All of this helps to improve healthcare and drive faster, more detailed and accurate clinical diagnosis.
If you need more information about our imaging solutions, just contact us and our staff will give you personalized advice.
Contact
BIbliography
Clínica Universidad de Navarra (n. d.). PACS. Medical dictionary. Retrieved from
https://www.cun.es/diccionario-medico/terminos/pacs
Ochoa, P. J., Murillo, M. R., & Torres, J. A. (2004). PACS system (picture archiving and transmission system). Anales de Radiología de México, 3(3), 153-162. https://www.analesderadiologiamexico.com/previos/ARM%202004%20Vol.%203/ARM_04_3_3_Julio-Septiembre/arm_04_3_3_153-162.pdf
López-Arroyo, A., Villarreal-García, A. J., & López-Arroyo, S. (2005). The DICOM format and PACS systems in medical imaging. Gaceta Médica de México, 141(5), 477-485. Retrieved from https://www.scielo.org.mx/pdf/gmm/v141n5/v141n5a11.pdf
Clinic Cloud (n. d.). DICOM format: what it is and how this standard works in medical imaging. Retrieved from https://clinic-cloud.com/blog/formato-dicom-que-es-estandar-imagenes-medicas
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.


por Kiko Ramos | Dec 10, 2024 | Projects
In collaboration with the Friends of Monkole Foundation in the Congo, 4D Medica has offered several teams and provided specific training to doctors to improve healthcare at Monkole Hospital, located in the Congo.
Monkole, Congo's hospital offering quality healthcare at no cost
Monkole Hospital is located in Mont-NgafulaThe region is a semi-urban area located south-west of Kinshasa, in the capital of the Democratic Republic of Congo. This region is made up of more than 300,000 low-income inhabitants. The Democratic Republic of Congo, with about 100 million inhabitants, ranks 180 out of 193 in the 2022 Human Development Index.
Its population is characterized by a lack of access to basic resources, such as food, housing and health care.. Thus, in addition to the lack of infrastructure and services, few inhabitants of the region can afford the health care they need. This is because, in the absence of Social Security, Health care and medical treatment are private and paid for.
Discover the history of Monkole: From its beginnings to the present day.
In view of the precarious situation in the Congo region, Monkole was established in 1991 as the first and only hospital in the Congo that began to care for and feed its patients.. It began as a dispensary with only one doctor, one laboratory assistant, three nurses and five other workers. Over the years, it evolved into a prestigious hospitalwhere the patients can access quality health care at no cost.. Therefore, if a person needs medical assistance and has no financial resources, Monkole will be able to provide the treatment he or she needs.
In the early days, there was a clear lack of infrastructure. Therefore, the directors of Monkole Hospital, with the help of the PATS program financed by the European Union, built a well and two electric generators in 1997. to have access to potable water and electricity. In turn, in order to solve the problem of hiring qualified personnel, CECFOR created a Instituto Superior de Enfermería (ISSI).
At 2001health care reform was developed in the country and Monkole was elevated to the rank of General Reference Hospital in the municipality of Mont-Ngafula. This was the beginning of the hospital expansion plans and currently offers a total of 120 beds and different medical specialties.
This is in addition to the help provided by the Friends of Monkole Foundationan entity that collaborates with the Monkole Hospital for to promote the health service. They offer humanitarian aid and cooperation so that the entire population can have access to health care, regardless of their resources and economic situation.
4D Medica's equipment and its partnership with Monkole Hospital
4D Medica has collaborated with the Friends of Monkole Foundation to provide medical equipment to the medical services of Monkole Hospital. Specifically, the following equipment was supplied and a training to the technical staff to make use of them:
Vieworks digital X-ray acquisition system
The equipment provided is the system for the acquisition of X-rays Vivix 4343 VW from Vieworks. It is an advanced flat panel detector designed for the capture of high quality digital radiographic images. By means of the flat panel technologyThe X-Ray X-Ray Detector uses a thin film transistor (TFT) matrix and photoconductive sensors for direct or indirect detection of X-rays. It has a size of 43 cm x 43 cm, making it ideal for full body X-rays.
Provides images with excellent sharpness that contributes to a accurate assessment and also has a wide dynamic range which has a superior contrast that helps differentiate the various anatomical structures. On the other hand, the model has a wireless connectivity via wifi which facilitates integration into different clinical environments and eliminates the need for cables. At the same time, it ensures PACS system integration and linkage with other medical devices.
Another aspect to be highlighted is that it provides a rapid acquisition of radiological images. Therefore, it uses less time between exposure and image display, which optimizes radiology workflows. Its low power consumption makes it an efficient medical equipment in terms of energy consumption and battery life.
It is an X-ray acquisition system that can be used in the radiology area and allows you to perform all types of studies: thorax, extremities, spine, spine and abdomen. It is compatible with both mobile X-ray systems and fixed configurations in radiology rooms.
4D Medica telemetry support
A telemetry stand manufactured by 4D Medica has also been included. This is a device or structure designed to house, organize and facilitate the handling of medical telemetry equipment in intensive care units (ICU), coronary units or transfer within medical facilities. This equipment is used for real-time monitoring of various physiological parameters such as cardiac activity, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation and other vital data.
As a portable model, they can be conveniently moved between different rooms and areas of the hospital. It is equipped with swivel casters and brakes for greater stability and control during use.
Imaging and telemedicine management software
The medical equipment supplied includes DxWorks image management software. Among its features, it stands out for being a fast and high quality image acquisition software which allows monitor system statusas well as storing and managing images in the database. In addition, it is compatible with the integration of the PACS system Vieworks QXLink 3 and allows for the remote operations planning.
The QXLink 3 image storage and display software is the QXLink 3, the PACS image archiving and communications system. Incorporates the storage of patient images in digital format and its main functions are the transmission, administration and consultation of the various medical files generated.
Siemens Siremóbil Compact L surgical arc
The following equipment is the Siemens Siremobil Compact L mobile fluoroscopy system. It is also known as a surgical arch and is designed to provide high quality images in real time during surgical and diagnostic procedures. It is used in specialties of traumatology, general surgery, urology, gynecology, cardiology and interventional medicine.
It is an equipment that has a integrated X-ray generator which allows precise images to be obtained with a controlled radiation dose. Its advanced technology provides a high resolution and good contrast to visualize the various anatomical details.
Another component of medical equipment is its intuitive control system and the dual monitor that provide access to a real-time display and the possibility of review previously captured images without interrupting the procedure. In addition, it includes an integrated memory for storing and retrieving images without the need for additional systems.
Orthopantomograph SATELEC Xmind
The Satelec X-Mind orthopantomograph is a dental X-ray equipment designed to capture high-quality panoramic imagesused in diagnostics and treatment planning in dentistry. The equipment has a high technology that helps to visualize the complete dentition in a single exposure, both the dentition and the maxillary bones and surrounding structures.
This medical equipment is used for general diagnosticsThe use of the instrument is also used for caries, infections and evaluation of bone structures. At the same time, it is also used for orthodontic, implantology and maxillofacial surgery treatment planning.
Specific training of the teams
From 4D Medica, a training of technical personnel on the use of the equipment to the different medical teams that collaborate with the Friends of Monkole Foundation. Specifically, it was explained the operation of the installed software in the equipment to be able to plan operations remotely from Spain.
Conclusion
In this project, 4D Medica has sent its medical teams to the Congo region to make health more accessible to its inhabitants. As specialists in the production and commercialization of medical solutions in the field of Diagnostic Imaging, 4D Medica has provided medical equipment with a high technology and high image resolution. In this way, the population with scarce resources will also be able to access quality medical diagnosis in different medical specialties and have access to the treatments and health care they need.
Kiko Ramos
CEO of 4D Medica. Expert in marketing and distribution of medical equipment.


por Luis Daniel Fernádez | Dec 5, 2024 | AI in medicine
The progress of new technologies has enabled a great evolution in the field of medicine. Nowadays, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a fundamental tool in different medical specialties, among which the area of image diagnosis. The integration of AI in medical diagnostics offers a multitude of benefits: increased accuracy and quality of diagnostics, early disease detection, task automation, workflow optimization, creation of personalized treatments and preventive measures.
Obtaining a rapid, accurate and effective diagnosis is a key aspect of achieving more efficient healthcare. The use of traditional methods involves the analysis of a large amount of data and the performance of tasks that involve a large amount of data. investment of time and resources. In addition to these aspects, there is also the limitation of the human subjectivityThe use of algorithms for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease, which can lead to errors in clinical practice. In this sense, the use of Artificial Intelligence in medicine has had a remarkable impact on diagnostic imaging. In the following article, we look at how AI that analyzes medical images works and its main applications.
Artificial Intelligence techniques in the analysis of medical images.
Artificial intelligence studies, designs and develops computerized computer systems based on algorithms. that can emulate some of the functions performed by humans, such as thinking and learning to solve problems. An algorithm consists of a set of computer instructions that are designed to perform a specific task. In recent years, a number of tools have emerged, such as the AI-enabled software that use artificial intelligence to automate many tasks and functions in the clinical setting.
What type of technology is used in medical imaging and how does it work? We can differentiate between different techniques:
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning (ML) is a field of artificial intelligence which consists of the use of computer algorithms to analyze and classify data, to learn from it and to make future predictions. The system must comply with a training phase which is referred to as supervised. During this process, medical images are entered with their corresponding, manually implemented labels. As more data is exposed, the algorithm learns to give a specific answer by evaluating different hand-labeled tests.
Most imaging systems make use of this type of artificial intelligence and it is important that, before using it in clinical practice, the system has been tested and validated. One of its main uses is to predict diseases at an early stage. For example, analyzing the probability that a breast lump visible on mammography is a malignant tumor.
Representational Learning or Representation Learning (RL)
Representation Learning (RL) is a sub-type of Machine Learning (ML) that does not require image features to be labeled by hand. Computer algorithm learns on its own the necessary characteristics to classify the data provided. Therefore, human subjectivity is eliminated, i.e., the limitation of analyzing those characteristics that the human being considers relevant. This system is called unsupervised learning and, if sufficient data is provided, the performance that can be obtained is superior to traditional ML.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning (DL) is an advanced form of Representation Learning (RL). This type of algorithm is in charge of exploring the use of artificial neural networks.based on the structure and function of the human brain. The artificial network of neurons is composed of different layers and connections. Through each layerIn addition, a series of data is propagated that is linked to the performance of a specific task.
In the area of diagnostic imaging, each layer is responsible for analyzing a characteristic of the medical image and assigning a value to it. Subsequently, the final layers of neurons are responsible for collecting all the information and providing a result. This type of technology has great potential and interest in medical image analysis, as it allows multiple uses. From the automatic detection of a lesion in the images and suggest differential diagnoses to structure a report in a preliminary way.
6 applications of AI in medical image analysis
Artificial Intelligence has the ability to process large amounts of data and recognize complex patterns. We can highlight the following applications in the field of diagnostic imaging:
1. Attendance at the radiologist's work
Power of Attorney manage patients' medical records electronically is a very important step forward, since it facilitates the work of the various medical teams involved in the diagnostic imaging process. AI can help to highlight the most relevant data and propose a specific planning of the study to provide information to the different professionals: the clinician, the technician and the radiologist.
2. Optimization of the radiological technique
Using Deep Learning (DL) methods, the algorithms allow for reconstruct images in medical techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging and computed axial tomography, or TAC. With this, the quality of medical images can be increased, making the most of the technical and physical resources available. Another advantage offered by AI is that it makes it possible to establish the ideal amount of radiation for each patient, avoiding the addition of unnecessary radiation.
3. Segmentation and lesion detection
Through the use of AI, the systems can understand the visualized images of an examination and differentiate healthy structures from pathological areas.
4. Classification and diagnosis of pathologies
There are different machine learning algorithms that can identify specific patterns and characteristics in medical imaging for classify them into different disease categories. Currently, algorithms are being developed for the detection of tumors in mammography images and skin cancer in dermoscopy images. In this field, AI can identify cancerous tissues and classify them into specific cancer types, which can lead to faster and more accurate diagnostics.
5. Prediction of treatment response
Artificial Intelligence can also predict patient response to different treatments. Algorithms can access patient data and medical studies with the diagnosis of the patient's disease. With all this information, the patient's response to various treatment options can be predicted. This offers many advantages, as the following can be developed specific treatment plans with a personalized approachadapted to the needs of each patient.
6. Early detection of diseases
Another of the applications of AI in medicine is the early detection of diseases. Through the analysis of large amounts of data, it is possible to detect patterns that may be missed by traditional techniques. For example, one of the uses recently offered by machine learning algorithms is to be able to detect early changes in magnetic resonance images of the brain, which may be indicative of diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusion
The AI-assisted medical diagnosis is evolving rapidly. Ongoing research is currently underway to refine existing AI models with the goal of exploring new applications to provide much more accurate, efficient and faster medical care.
Bibliography
Cuevas Editores (s. f.).
Imaging: Volume 5 (p. 22). Retrieved from
https://cuevaseditores.com/libros/diciembre/imagenologiavol5.pdf#page=22
Durán, L., & Gutiérrez, M. (2020). Imaging: Technical fundamentals and medical application. Vitalia, 8(2), 183-278. Retrieved from https://revistavitalia.org/index.php/vitalia/article/view/183/278
Radiological Society of Uruguay (2021). Radiology and technological innovation in Latin America. Journal of Diagnostic Imaging, 4(1), 53-63. Retrieved from https://www.sriuy.org.uy/ojs/index.php/Rdi/article/view/53/63
Radiological Society of Uruguay (2022). New trends in diagnostic radiology. Journal of Diagnostic Imaging, 5(2). Retrieved from https://www.sriuy.org.uy/ojs/index.php/Rdi/article/view/94
Fernández, J., & Salazar, A. (2023). Advances in medical imaging techniques. Latin Science, 7(3), Article 13751. Retrieved from https://www.ciencialatina.org/index.php/cienciala/article/view/13751
Luis Daniel Fernandez Perez
Director of Diagximag. Distributor of medical imaging equipment and solutions.